5'-Phospho-RNA Acceptor Specificity of GDP Polyribonucleotidyltransferase of Vesicular Stomatitis Virus in mRNA Capping
- PMID: 28053102
- PMCID: PMC5331801
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02322-16
5'-Phospho-RNA Acceptor Specificity of GDP Polyribonucleotidyltransferase of Vesicular Stomatitis Virus in mRNA Capping
Abstract
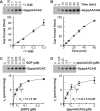
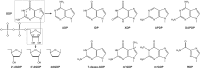
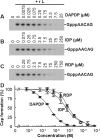
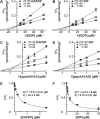
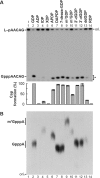
The GDP polyribonucleotidyltransferase (PRNTase) domain of the multifunctional L protein of rhabdoviruses, such as vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) and rabies virus, catalyzes the transfer of 5'-phospho-RNA (pRNA) from 5'-triphospho-RNA (pppRNA) to GDP via a covalent enzyme-pRNA intermediate to generate a 5'-cap structure (GpppA). Here, using an improved oligo-RNA capping assay with the VSV L protein, we showed that the Michaelis constants for GDP and pppAACAG (VSV mRNA-start sequence) are 0.03 and 0.4 μM, respectively. A competition assay between GDP and GDP analogues in the GpppA formation and pRNA transfer assay using GDP analogues as pRNA acceptors indicated that the PRNTase domain recognizes the C-2-amino group, but not the C-6-oxo group, N-1-hydrogen, or N-7-nitrogen, of GDP for the cap formation. 2,6-Diaminopurine-riboside (DAP), 7-deazaguanosine (7-deaza-G), and 7-methylguanosine (m7G) diphosphates efficiently accepted pRNA, resulting in the formation of DAPpppA, 7-deaza-GpppA, and m7GpppA (cap 0), respectively. Furthermore, either the 2'- or 3'-hydroxyl group of GDP was found to be required for efficient pRNA transfer. A 5'-diphosphate form of antiviral ribavirin weakly inhibited the GpppA formation but did not act as a pRNA acceptor. These results indicate that the PRNTase domain has a unique guanosine-binding mode different from that of eukaryotic mRNA capping enzyme, guanylyltransferase. IMPORTANCE mRNAs of nonsegmented negative-strand (NNS) RNA viruses, such as VSV, possess a fully methylated cap structure, which is required for mRNA stability, efficient translation, and evasion of antiviral innate immunity in host cells. GDP polyribonucleotidyltransferase (PRNTase) is an unconventional mRNA capping enzyme of NNS RNA viruses that is distinct from the eukaryotic mRNA capping enzyme, guanylyltransferase. In this study, we studied the pRNA acceptor specificity of VSV PRNTase using various GDP analogues and identified chemical groups of GDP as essential for the substrate activity. The findings presented here are useful not only for understanding the mechanism of the substrate recognition with PRNTase but also for designing antiviral agents targeting this enzyme.
Keywords: GDP polyribonucleotidyltransferase; L protein; cap structure; mRNA capping; nonsegmented negative-strand RNA viruses; rabies virus; vesicular stomatitis virus.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

References
-
- Ogino T, Banerjee AK. 2011. mRNA capping by vesicular stomatitis virus and other related viruses, p 79–94. In Luo M. (ed), Negative strand RNA virus. World Scientific, Singapore.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

