Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded Latent Membrane Protein 1 Upregulates Glucose Transporter 1 Transcription via the mTORC1/NF-κB Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 28053105
- PMCID: PMC5331802
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02168-16
Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded Latent Membrane Protein 1 Upregulates Glucose Transporter 1 Transcription via the mTORC1/NF-κB Signaling Pathways
Abstract
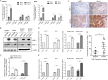
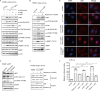
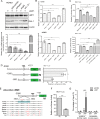
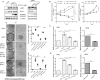
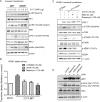
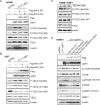
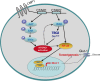
Accumulating evidence indicates that oncogenic viral protein plays a crucial role in activating aerobic glycolysis during tumorigenesis, but the underlying mechanisms are largely undefined. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) is a transmembrane protein with potent cell signaling properties and has tumorigenic transformation property. Activation of NF-κB is a major signaling pathway mediating many downstream transformation properties of LMP1. Here we report that activation of mTORC1 by LMP1 is a key modulator for activation of NF-κB signaling to mediate aerobic glycolysis. NF-κB activation is involved in the LMP1-induced upregulation of glucose transporter 1 (Glut-1) transcription and growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cells. Blocking the activity of mTORC1 signaling effectively suppressed LMP1-induced NF-κB activation and Glut-1 transcription. Interfering NF-κB signaling had no effect on mTORC1 activity but effectively altered Glut-1 transcription. Luciferase promoter assay of Glut-1 also confirmed that the Glut-1 gene is a direct target gene of NF-κB signaling. Furthermore, we demonstrated that C-terminal activating region 2 (CTAR2) of LMP1 is the key domain involved in mTORC1 activation, mainly through IKKβ-mediated phosphorylation of TSC2 at Ser939 Depletion of Glut-1 effectively led to suppression of aerobic glycolysis, inhibition of cell proliferation, colony formation, and attenuation of tumorigenic growth property of LMP1-expressing nasopharyngeal epithelial (NPE) cells. These findings suggest that targeting the signaling axis of mTORC1/NF-κB/Glut-1 represents a novel therapeutic target against NPC.IMPORTANCE Aerobic glycolysis is one of the hallmarks of cancer, including NPC. Recent studies suggest a role for LMP1 in mediating aerobic glycolysis. LMP1 expression is common in NPC. The delineation of essential signaling pathways induced by LMP1 in aerobic glycolysis contributes to the understanding of NPC pathogenesis. This study provides evidence that LMP1 upregulates Glut-1 transcription to control aerobic glycolysis and tumorigenic growth of NPC cells through mTORC1/NF-κB signaling. Our results reveal novel therapeutic targets against the mTORC1/NF-κB/Glut-1 signaling axis in the treatment of EBV-infected NPC.
Keywords: Glut-1; LMP1; NF-κB; mTORC1; nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
NF-κB Signaling Regulates Expression of Epstein-Barr Virus BART MicroRNAs and Long Noncoding RNAs in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.J Virol. 2016 Jun 24;90(14):6475-88. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00613-16. Print 2016 Jul 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27147748 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the FGFR1 signalling pathway by the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP1 promotes aerobic glycolysis and transformation of human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells.J Pathol. 2015 Oct;237(2):238-48. doi: 10.1002/path.4575. Epub 2015 Aug 3. J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26096068
-
Induction of epidermal growth factor receptor expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 C-terminal-activating region 1 is mediated by NF-kappaB p50 homodimer/Bcl-3 complexes.J Virol. 2007 Dec;81(23):12954-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01601-07. Epub 2007 Sep 19. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17881446 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Epstein-Barr virus encoded latent membrane protein 1 in the carcinogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cell Mol Immunol. 2007 Jun;4(3):185-96. Cell Mol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17601372 Review.
-
Novel roles and therapeutic targets of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1-induced oncogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2015 Aug 18;17:e15. doi: 10.1017/erm.2015.13. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26282825 Review.
Cited by
-
The Influence of Metabolism on Immune Response: A Journey to Understand Immunometabolism in the Context of Viral Infection.Viruses. 2023 Dec 9;15(12):2399. doi: 10.3390/v15122399. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38140640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral hijacking of cellular metabolism.BMC Biol. 2019 Jul 18;17(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12915-019-0678-9. BMC Biol. 2019. PMID: 31319842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the NFκB-signaling pathway in cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Apr 11;11:2063-2073. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S161109. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 29695914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNMT1 mediates metabolic reprogramming induced by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 and reversed by grifolin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2018 May 23;9(6):619. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0662-2. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29795311 Free PMC article.
-
Revving the engine: PKB/AKT as a key regulator of cellular glucose metabolism.Front Physiol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1320964. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1320964. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38264327 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cheng SH, Tsai SY, Yen KL, Jian JJ-M, Chu N-M, Chan K-Y, Tan T-D, Cheng JC, Hsieh C-Y, Huang AT. 2000. Concomitant radiotherapy and chemotherapy for early-stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 18:2040–2045. - PubMed
-
- Trivedi P, Hu LF, Chen F, Masucci M, Klein G, Winberg G, Christensson B. 1994. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded membrane protein LMP1 from a nasopharyngeal carcinoma is non-immunogenic in a murine model system, in contrast to a B cell-derived homologue. Eur J Cancer 30:84–88. doi:10.1016/S0959-8049(05)80024-3. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

