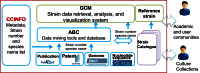
World data centre for microorganisms: an information infrastructure to explore and utilize preserved microbial strains worldwide
- PMID: 28053166
- PMCID: PMC5210620
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw903
World data centre for microorganisms: an information infrastructure to explore and utilize preserved microbial strains worldwide
Abstract
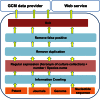
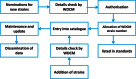
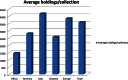
The World Data Centre for Microorganisms (WDCM) was established 50 years ago as the data center of the World Federation for Culture Collections (WFCC)-Microbial Resource Center (MIRCEN). WDCM aims to provide integrated information services using big data technology for microbial resource centers and microbiologists all over the world. Here, we provide an overview of WDCM including all of its integrated services. Culture Collections Information Worldwide (CCINFO) provides metadata information on 708 culture collections from 72 countries and regions. Global Catalogue of Microorganism (GCM) gathers strain catalogue information and provides a data retrieval, analysis, and visualization system of microbial resources. Currently, GCM includes >368 000 strains from 103 culture collections in 43 countries and regions. Analyzer of Bioresource Citation (ABC) is a data mining tool extracting strain related publications, patents, nucleotide sequences and genome information from public data sources to form a knowledge base. Reference Strain Catalogue (RSC) maintains a database of strains listed in International Standards Organization (ISO) and other international or regional standards. RSC allocates a unique identifier to strains recommended for use in diagnosis and quality control, and hence serves as a valuable cross-platform reference. WDCM provides free access to all these services at www.wdcm.org.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- David S. Culture collections over the world. Int. Microbiol. 2003;6:95–100. - PubMed
-
- WFCC Executive Board. World Federation for Culture Collections Guidelines. 3rd edn. 2010. http://www.wfcc.info/guidelines/
-
- Skerman V.B.D. World Directory of Collections of Cultures of Microorganisms. NY: John Wiley Sons, Inc; 1972.
-
- Satoru M., Hideaki S. Networking of biological resource centres: WDCM experiences. Data Sci. J. 2002;1:229–234.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources