Increased autophagy in fibroblast-like synoviocytes leads to immune enhancement potential in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 28053286
- PMCID: PMC5362496
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14331
Increased autophagy in fibroblast-like synoviocytes leads to immune enhancement potential in rheumatoid arthritis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Increased autophagy in fibroblast-like synoviocytes leads to immune enhancement potential in rheumatoid arthritis.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 21;8(34):57906. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20371. eCollection 2017 Aug 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28915723 Free PMC article.
Abstract
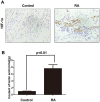
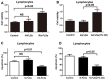
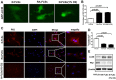
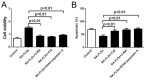
The incidence of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has been reported to be correlated with a disorder of immunregulation. Rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RA-FLSs) play an important role in regulating the local immune microenvironment. However, the potential mechanism of RA-FLS in regulating the immnue response is not clearly understood. In this study, we demonstrated that the expression of HIF-1α was significantly up-regulated in rheumatoid arthritis tissue which indicated that the hypoxia condition in the microenvironment. We also observed that RA-FLSs demonstrated the potential to up-regulate immune activation. Meanwhile, the level of autophagy increased in RA-FLSs compared with control group. Besides that, the expression of IL-6 was up-regulated not only in RA-FLSs but also in the fibroblasts that treated with hypoxia condition. Accordingly, we found that autophagy inhibitiors could effectively inhibit the immune activation function of RA-FLSs medicated by IL-6. Taken together, the results we demonstrated above indicated that the hypoxia microenvironment could effectively induce the incidence of autophagy and then lead to the immune activation function of RA-FLSs medicated by IL-6.
Keywords: IL-6; autophagy; fibroblast-like synoviocytes; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
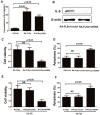
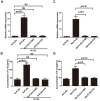
References
-
- Hoppe B, Haupl T, Egerer K, Gruber R, Kiesewetter H, Salama A, Burmester GR, Dorner T. Influence of peptidylarginine deiminase type 4 genotype and shared epitope on clinical characteristics and autoantibody profile of rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2009;68:898–903. - PubMed
-
- Anzilotti C, Pratesi F, Tommasi C, Migliorini P. Peptidylarginine deiminase 4 and citrullination in health and disease. Autoimmunity reviews. 2010;9:158–160. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki A, Yamada R, Chang X, Tokuhiro S, Sawada T, Suzuki M, Nagasaki M, Nakayama-Hamada M, Kawaida R, et al. Functional haplotypes of PADI4, encoding citrullinating enzyme peptidylarginine deiminase 4, are associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Nature genetics. 2003;34:395–402. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

