Motor evoked potential and voluntary EMG activity after olfactory mucosal autograft transplantation in a case of chronic, complete spinal cord injury: case report
- PMID: 28053727
- PMCID: PMC5125064
- DOI: 10.1038/scsandc.2015.18
Motor evoked potential and voluntary EMG activity after olfactory mucosal autograft transplantation in a case of chronic, complete spinal cord injury: case report
Erratum in
-
Erratum for Spinal Cord Series and Cases content published prior to July 2016.Spinal Cord Ser Cases. 2016 Jul 21;2:16019. doi: 10.1038/scsandc.2016.19. eCollection 2016. Spinal Cord Ser Cases. 2016. PMID: 31265710 Free PMC article.
Abstract
The efficacy of olfactory mucosal autografts (OMAs) for chronic spinal cord injury (SCI) has been reported, but there is no report documenting electrophysiological conductivity via the emergence of motor evoked potentials (MEPs). We report the case of a 39-year-old man with chronic, complete SCI at T8, who exhibited MEPs after OMA transplantation, and, with intensive rehabilitation, was ultimately able to ambulate with short leg braces and Lofstrand crutches. The initial injury occurred in a motor vehicle accident in November 1999 and resulted in a complete loss of sensorimotor function below T8. OMA transplantation to the injury site was performed in March 2010 in combination with intensive pre- and postoperative rehabilitation. The patient exhibited voluntary electromyograph (EMG) activity and MEPs at 96 and 144 weeks after transplantation and he was was ambulatory with short leg braces and Lofstrand crutches at 144 weeks after transplantation. We were able to elicit MEPs after OMA with intensive rehabilitation. To our knowledge, this is the first report of recovery of electrophysiological conductivity in the spinal cord after any type of treatment for chronic, complete SCI.
Figures
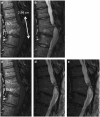


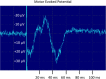
References
-
- Calof AL , Bonnin A , Crocker C , Kawauchi S , Murray RC , Shou J et al. Progenitor cells of the olfactory receptor neuron lineage. Microsc Res Tech 2002; 58: 176–188. - PubMed
-
- Roisen FJ , Klueber KM , Lu CL , Hatcher LM , Dozier A , Shields CB et al. Adult human olfactory stem cells. Brain Res 2001; 890: 11–22. - PubMed
-
- Smith PM , Lakatos A , Barnett SC , Jeffery ND , Franklin RJ . Cryopreserved cells isolated from the adult canine olfactory bulb are capable of extensive remyelination following transplantation into the adult rat CNS. Exp Neurol 2002; 176: 402–406. - PubMed
-
- Feron F , Perry C , McGrath JJ , Mackay-Sim AF . New techniques for biopsy and culture of human olfactory epithelial neurons. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1998; 124: 861–866. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

