Management of mid-shaft clavicular fractures: comparison between non-operative treatment and plate fixation in 60 patients
- PMID: 28054249
- PMCID: PMC5360671
- DOI: 10.1007/s11751-016-0272-4
Management of mid-shaft clavicular fractures: comparison between non-operative treatment and plate fixation in 60 patients
Abstract
Clavicle fracture is a common injury due to its subcutaneous and relatively anterior position. Fractures affecting the middle third account for majority of all clavicular fractures. Both non-operative and surgical methods have been described for the management of this injury. However, there is no uniform consensus on the definite choice of treatment. Hence, this study was undertaken to compare conservative approach with primary internal plate fixation in mid-shaft clavicular fractures in terms of subjective outcome, functional outcome, the rates of nonunion and malunion and other local complications. Patients were allocated into two groups, each including 30 patients on alternate basis. Group 1 patients were managed conservatively, consisting of a figure-of-eight bandage and a sling, whereas patients of group 2 were treated surgically by plate fixation. Follow-up examination was done at 06 weeks, 03 and 06 months using patient's subjective evaluation, functional outcome, radiographic assessment and other complications. The study showed that time to union was significantly shorter in patients treated surgically and this group also showed a favorable Constant shoulder score at all follow-ups. Though there was no statistically significant difference between the groups with regard to complication rate, subjective outcome or functional outcome, the surgical intervention group fared better especially when considering overall outcome results. The present study showed that the time to union was lesser, rate of malunion and nonunion was lower, and Constant shoulder scores were higher in the surgical group. This affirms that while conservative treatment remains the treatment of choice for simple undisplaced mid-shaft clavicle fractures, for displaced and comminuted fractures the surgical intervention gives better outcomes and early functional recovery in young active adults.
Keywords: Clavicle; Fracture; Mid-shaft; Plating.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Figures

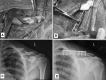

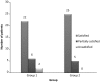
References
-
- Curtis RJ, Dameron TB, Rockwood CA. Fractures and dislocations of the shoulder in children. In: Rockwood CA, Wilkins KE, King RE, editors. Fractures in children. 3. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 1991. pp. 829–919.
-
- Craig EV. Fractures of the clavicle. In: Rockwood CA, Matsen FA, editors. The shoulder. 3. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1998. pp. 428–482.
-
- Nordqvist A, Petersson C. The incidence of fractures of the clavicle. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;300:127–132. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

