Molecular control of Rab activity by GEFs, GAPs and GDI
- PMID: 28055292
- PMCID: PMC5902221
- DOI: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1276999
Molecular control of Rab activity by GEFs, GAPs and GDI
Abstract
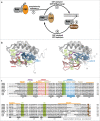
Rab proteins are the major regulators of vesicular trafficking in eukaryotic cells. Their activity can be tightly controlled within cells: Regulated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) and GTPase activating proteins (GAPs), they switch between an active GTP-bound state and an inactive GDP-bound state, interacting with downstream effector proteins only in the active state. Additionally, they can bind to membranes via C-terminal prenylated cysteine residues and they can be solubilized and shuttled between membranes by chaperone-like molecules called GDP dissociation inhibitors (GDIs). In this review we give an overview of Rab proteins with a focus on the current understanding of their regulation by GEFs, GAPs and GDI.
Keywords: GAPS; GDI; GEFs; Rab proteins; intracellular trafficking; posttranslational modifications; vesicular transport.
Figures



References
-
- Barr F, Lambright DG. Rab GEFs and GAPs. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2010; 22(4):461-70; PMID:20466531; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2010.04.007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stenmark H. Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009; 10(8):513-25; PMID:19603039; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrm2728 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Novick P, Field C, Schekman R. Identification of 23 complementation groups required for post-translational events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell 1980; 21(1):205-15; PMID:6996832; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(80)90128-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Salminen A, Novick PJ. A ras-like protein is required for a post-Golgi event in yeast secretion. Cell 1987; 49(4):527-38; PMID:3552249; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(87)90455-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schmitt HD, Wagner P, Pfaff E, Gallwitz D. The ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast: a GTP-binding protein that might be involved in microtubule organization. Cell 1986; 47(3):401-12; PMID:3094963; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(86)90597-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
