Association of Delayed Adjuvant Chemotherapy With Survival After Lung Cancer Surgery
- PMID: 28056112
- PMCID: PMC5824207
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5829
Association of Delayed Adjuvant Chemotherapy With Survival After Lung Cancer Surgery
Abstract
Importance: Adjuvant chemotherapy offers a survival benefit to a number of staging scenarios in non-small-cell lung cancer. Variable recovery from lung cancer surgery may delay a patient's ability to tolerate adjuvant chemotherapy, yet the urgency of chemotherapy initiation is unclear.
Objective: To assess differences in survival according to the time interval between non-small-cell lung cancer resection and the initiation of postoperative chemotherapy to determine the association between adjuvant treatment timing and efficacy.
Design, setting, and participants: This retrospective observational study examined treatment-naive patients with completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer who received postoperative multiagent chemotherapy between 18 and 127 days after resection between January 2004 and December 2012. The study population was limited to patients with lymph node metastases, tumors 4 cm or larger, or local extension. Patients were identified from the National Cancer Database, a hospital-based tumor registry that captures more than 70% of incident lung cancer cases in the United States. The association between time to initiation of adjuvant chemotherapy and survival was evaluated using Cox models with restricted cubic splines.
Exposures: Adjuvant chemotherapy administered at different time points after surgery.
Main outcomes and measures: Effectiveness of adjuvant chemotherapy according to time to initiation after surgery.
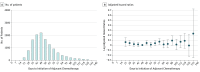
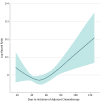
Results: A total of 12 473 patients (median [interquartile range] age, 64 [57-70] years) were identified: 3073 patients (25%) with stage I disease; 5981 patients (48%), stage II; and 3419 patients (27%), stage III. A Cox model with restricted cubic splines identified the lowest mortality risk when chemotherapy was started 50 days postoperatively (95% CI, 39-56 days). Initiation of chemotherapy after this interval (57-127 days; ie, the later cohort) did not increase mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 1.037; 95% CI, 0.972-1.105; P = .27). Furthermore, in a Cox model of 3976 propensity-matched pairs, patients who received chemotherapy during the later interval had a lower mortality risk than those treated with surgery only (HR, 0.664; 95% CI, 0.623-0.707; P < .001).
Conclusions and relevance: In the National Cancer Database, adjuvant chemotherapy remained efficacious when started 7 to 18 weeks after non-small-cell lung cancer resection. Patients who recover slowly from non-small-cell lung cancer surgery may still benefit from delayed adjuvant chemotherapy started up to 4 months after surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Bringing Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Resected Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Into Real-world Practice-Better Late Than Never?JAMA Oncol. 2017 May 1;3(5):619. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5798. JAMA Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28056130 No abstract available.
-
Delayed Adjuvant Chemotherapy and Survival After Lung Cancer Surgery.JAMA Oncol. 2018 Feb 1;4(2):262. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0167. JAMA Oncol. 2018. PMID: 28975199 No abstract available.
-
Delayed Adjuvant Chemotherapy and Survival After Lung Cancer Surgery-Reply.JAMA Oncol. 2018 Feb 1;4(2):262-263. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.2760. JAMA Oncol. 2018. PMID: 28975275 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mohammed N, Kestin LL, Grills IS, et al. Rapid Disease Progression With Delay in Treatment of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;79(2):466-472. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(1):7-30. - PubMed
-
- Arriagada R, Bergman B, Dunant A, Le Chevalier T, Pignon JP, Vansteenkiste J; International Adjuvant Lung Cancer Trial Collaborative Group . Cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(4):351-360. - PubMed
-
- Winton T, Livingston R, Johnson D, et al. ; National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group; National Cancer Institute of the United States Intergroup JBR.10 Trial Investigators . Vinorelbine plus cisplatin vs. observation in resected non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(25):2589-2597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

