Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 28057046
- PMCID: PMC5217326
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-016-0794-1
Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The presence of a high neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been associated with increased mortality in several malignancies. Here, we quantify the effect of NLR on survival in patients with breast cancer, and examine the effect of clinicopathologic factors on its prognostic value.
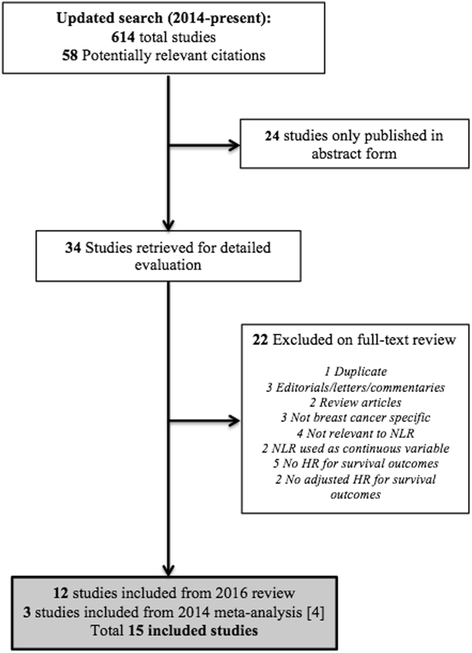
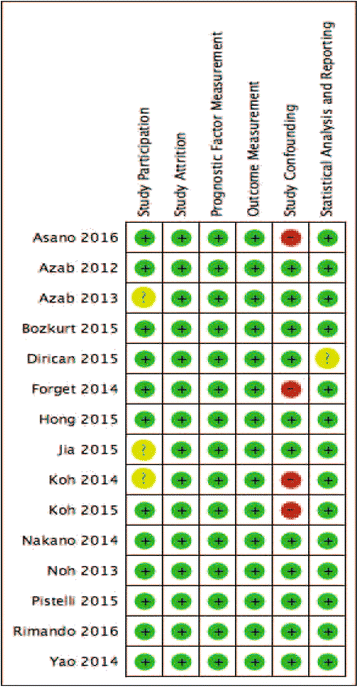
Methods: A systematic search of electronic databases was conducted to identify publications exploring the association of blood NLR (measured pre treatment) and overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) among patients with breast cancer. Data from studies reporting a hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) or a P value were pooled in a meta-analysis. Pooled HRs were computed and weighted using generic inverse variance. Meta-regression was performed to evaluate the influence of clinicopathologic factors such as age, disease stage, tumor grade, nodal involvement, receptor status, and NLR cutoff on the HR for OS and DFS. All statistical tests were two-sided.
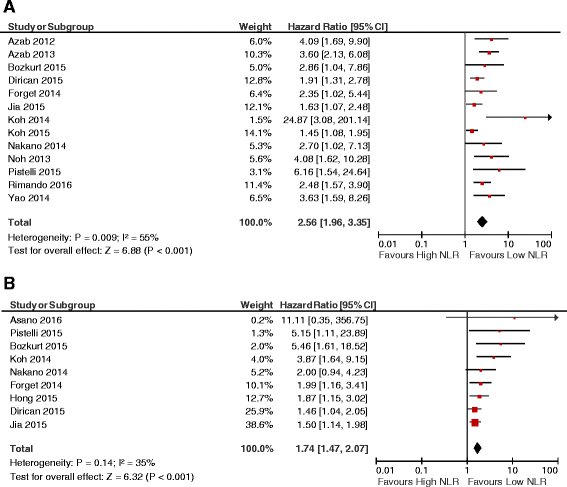
Results: Fifteen studies comprising a total of 8563 patients were included. The studies used different cutoff values to classify high NLR (range 1.9-5.0). The median cutoff value for high NLR used in these studies was 3.0 amongst 13 studies reporting a HR for OS, and 2.5 in 10 studies reporting DFS outcomes. NLR greater than the cutoff value was associated with worse OS (HR 2.56, 95% CI = 1.96-3.35; P < 0.001) and DFS (HR 1.74, 95% CI = 1.47-2.07; P < 0.001). This association was similar in studies including only early-stage disease and those comprising patients with both early-stage and metastatic disease. Estrogen receptor (ER) and HER-2 appeared to modify the effect of NLR on DFS, because NLR had greater prognostic value for DFS in ER-negative and HER2-negative breast cancer. No subgroup showed an influence on the association between NLR and OS.
Conclusions: High NLR is associated with an adverse OS and DFS in patients with breast cancer with a greater effect on disease-specific outcome in ER and HER2-negative disease. NLR is an easily accessible prognostic marker, and its addition to established risk prediction models warrants further investigation.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Disease-free survival; Meta-analysis; Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; Overall survival; Prognosis; Systematic review.
Figures
References
-
- Templeton AJ, McNamara MG, Seruga B, Vera-Badillo FE, Aneja P, Ocana A, Leibowitz-Amit R, Sonpavde G, Knox JJ, Tran B, Tannock IF, Amir E. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106(6):dju124. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju124. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

