A population of hematopoietic stem cells derives from GATA4-expressing progenitors located in the placenta and lateral mesoderm of mice
- PMID: 28057738
- PMCID: PMC5395105
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2016.155812
A population of hematopoietic stem cells derives from GATA4-expressing progenitors located in the placenta and lateral mesoderm of mice
Abstract
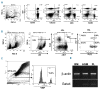
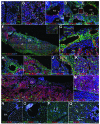
GATA transcription factors are expressed in the mesoderm and endoderm during development. GATA1-3, but not GATA4, are critically involved in hematopoiesis. An enhancer (G2) of the mouse Gata4 gene directs its expression throughout the lateral mesoderm and the allantois, beginning at embryonic day 7.5, becoming restricted to the septum transversum by embryonic day 10.5, and disappearing by midgestation. We have studied the developmental fate of the G2-Gata4 cell lineage using a G2-Gata4Cre;R26REYFP mouse line. We found a substantial number of YFP+ hematopoietic cells of lymphoid, myeloid and erythroid lineages in embryos. Fetal CD41+/cKit+/CD34+ and Lin-/cKit+/CD31+ YFP+ hematopoietic progenitors were much more abundant in the placenta than in the aorta-gonad-mesonephros area. They were clonogenic in the MethoCult assay and fully reconstituted hematopoiesis in myeloablated mice. YFP+ cells represented about 20% of the hematopoietic system of adult mice. Adult YFP+ hematopoietic stem cells constituted a long-term repopulating, transplantable population. Thus, a lineage of adult hematopoietic stem cells is characterized by the expression of GATA4 in their embryonic progenitors and probably by its extraembryonic (placental) origin, although GATA4 appeared not to be required for hematopoietic stem cell differentiation. Both lineages basically showed similar physiological behavior in normal mice, but clinically relevant properties of this particular hematopoietic stem cell population should be checked in physiopathological conditions.
Copyright© Ferrata Storti Foundation.
Figures
References
-
- Kuo CT, Morrisey EE, Anandappa R, et al. GATA4 transcription factor is required for ventral morphogenesis and heart tube formation. Genes Dev. 1997;11(8):1048–1060. - PubMed
-
- Molkentin JD, Lin Q, Duncan SA, Olson EN. Requirement of the transcription factor GATA4 for heart tube formation and ventral morphogenesis. Genes Dev. 1997; 11(8):1061–1072. - PubMed
-
- Narita N, Bielinska M, Wilson DB. Wild-type endoderm abrogates the ventral developmental defects associated with GATA-4 deficiency in the mouse. Dev Biol. 1997;189(2):270–274. - PubMed
-
- Rojas A, De Val S, Heidt AB, Xu SM, Bristow J, Black BL. Gata4 expression in lateral mesoderm is downstream of BMP4 and is activated directly by Forkhead and GATA transcription factors through a distal enhancer element. Development. 2005;132(15):3405–3417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

