Protein Interactions at Endothelial Junctions and Signaling Mechanisms Regulating Endothelial Permeability
- PMID: 28057793
- PMCID: PMC5225667
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.306534
Protein Interactions at Endothelial Junctions and Signaling Mechanisms Regulating Endothelial Permeability
Abstract
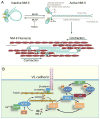
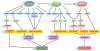
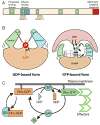
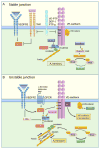
The monolayer of endothelial cells lining the vessel wall forms a semipermeable barrier (in all tissue except the relatively impermeable blood-brain and inner retinal barriers) that regulates tissue-fluid homeostasis, transport of nutrients, and migration of blood cells across the barrier. Permeability of the endothelial barrier is primarily regulated by a protein complex called adherens junctions. Adherens junctions are not static structures; they are continuously remodeled in response to mechanical and chemical cues in both physiological and pathological settings. Here, we discuss recent insights into the post-translational modifications of junctional proteins and signaling pathways regulating plasticity of adherens junctions and endothelial permeability. We also discuss in the context of what is already known and newly defined signaling pathways that mediate endothelial barrier leakiness (hyperpermeability) that are important in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular and lung diseases and vascular inflammation.
Keywords: adherens junctions; blood cells; endothelial cells; lung diseases; signal transduction.
© 2017 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures


Comment in
-
Letter by Horowitz Regarding Article, "Protein Interactions at Endothelial Junctions and Signaling Mechanisms Regulating Endothelial Permeability".Circ Res. 2017 Mar 3;120(5):e27. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.310613. Circ Res. 2017. PMID: 28254807 No abstract available.
-
Response by Komarova et al to Letter Regarding Article, "Protein Interactions at Endothelial Junctions and Signaling Mechanisms Regulating Endothelial Permeability".Circ Res. 2017 Mar 3;120(5):e28. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.310647. Circ Res. 2017. PMID: 28254808 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Pappenheimer JR, Renkin EM, Borrero LM. Filtration, diffusion and molecular sieving through peripheral capillary membranes; a contribution to the pore theory of capillary permeability. The American journal of physiology. 1951;167:13–46. - PubMed
-
- Del Vecchio PJ, Siflinger-Birnboim A, Shepard JM, Bizios R, Cooper JA, Malik AB. Endothelial monolayer permeability to macromolecules. Federation proceedings. 1987;46:2511–2515. - PubMed
-
- Siflinger-Birnboim A, Del Vecchio PJ, Cooper JA, Blumenstock FA, Shepard JM, Malik AB. Molecular sieving characteristics of the cultured endothelial monolayer. J Cell Physiol. 1987;132:111–117. - PubMed
-
- Schneeberger EE. Circulating proteins and macromolecular transport across continuous, nonfenestrated endothelium. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1982;401:25–37. - PubMed
-
- Weisberg HF. Osmotic pressure of the serum proteins. Annals of clinical and laboratory science. 1978;8:155–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

