Scaling of titanium implants entrains inflammation-induced osteolysis
- PMID: 28059080
- PMCID: PMC5216395
- DOI: 10.1038/srep39612
Scaling of titanium implants entrains inflammation-induced osteolysis
Abstract
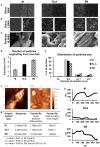
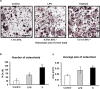
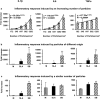
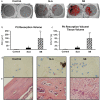
With millions of new dental and orthopedic implants inserted annually, periprosthetic osteolysis becomes a major concern. In dentistry, peri-implantitis management includes cleaning using ultrasonic scaling. We examined whether ultrasonic scaling releases titanium particles and induces inflammation and osteolysis. Titanium discs with machined, sandblasted/acid-etched and sandblasted surfaces were subjected to ultrasonic scaling and we physically and chemically characterized the released particles. These particles induced a severe inflammatory response in macrophages and stimulated osteoclastogenesis. The number of released particles and their chemical composition and nanotopography had a significant effect on the inflammatory response. Sandblasted surfaces released the highest number of particles with the greatest nanoroughness properties. Particles from sandblasted/acid-etched discs induced a milder inflammatory response than those from sandblasted discs but a stronger inflammatory response than those from machined discs. Titanium particles were then embedded in fibrin membranes placed on mouse calvariae for 5 weeks. Using micro-CT, we observed that particles from sandblasted discs induced more osteolysis than those from sandblasted/acid-etched discs. In summary, ultrasonic scaling of titanium implants releases particles in a surface type-dependent manner and may aggravate peri-implantitis. Future studies should assess whether surface roughening affects the extent of released wear particles and aseptic loosening of orthopedic implants.
Figures
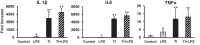
References
-
- Heitz-Mayfield L. J., Needleman I., Salvi G. E. & Pjetursson B. E. Consensus statements and clinical recommendations for prevention and management of biologic and technical implant complications. International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 29 Suppl, 346–350, doi: 10.11607/jomi.2013.g5 (2014). - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

