Regeneration of fat cells from myofibroblasts during wound healing
- PMID: 28059714
- PMCID: PMC5464786
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aai8792
Regeneration of fat cells from myofibroblasts during wound healing
Abstract
Although regeneration through the reprogramming of one cell lineage to another occurs in fish and amphibians, it has not been observed in mammals. We discovered in the mouse that during wound healing, adipocytes regenerate from myofibroblasts, a cell type thought to be differentiated and nonadipogenic. Myofibroblast reprogramming required neogenic hair follicles, which triggered bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling and then activation of adipocyte transcription factors expressed during development. Overexpression of the BMP antagonist Noggin in hair follicles or deletion of the BMP receptor in myofibroblasts prevented adipocyte formation. Adipocytes formed from human keloid fibroblasts either when treated with BMP or when placed with human hair follicles in vitro. Thus, we identify the myofibroblast as a plastic cell type that may be manipulated to treat scars in humans.
Copyright © 2017, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures

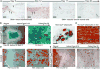
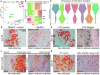
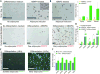
Comment in
-
Fibroblasts become fat to reduce scarring.Science. 2017 Feb 17;355(6326):693-694. doi: 10.1126/science.aam6748. Science. 2017. PMID: 28209860 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Repeal and Replace: Adipocyte Regeneration in Wound Repair.Cell Stem Cell. 2017 Apr 6;20(4):424-426. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2017.03.015. Cell Stem Cell. 2017. PMID: 28388424
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI047833/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR059768/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR066022/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR067273/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR069589/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009054/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR055309/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AR047709/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR069653/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 GM111100/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR064184/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK104789/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK103008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM095821/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK049780/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK049210/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR057217/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK019525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM055246/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

