Control of nuclear organization by F-actin binding proteins
- PMID: 28060557
- PMCID: PMC5403142
- DOI: 10.1080/19491034.2016.1267093
Control of nuclear organization by F-actin binding proteins
Abstract
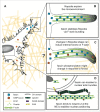
The regulation of nuclear shape and deformability is a key factor in controlling diverse events from embryonic development to cancer cell metastasis, but the mechanisms governing this process are still unclear. Our recent study demonstrated an unexpected role for the F-actin bundling protein fascin in controlling nuclear plasticity through a direct interaction with Nesprin-2. Nesprin-2 is a component of the LINC complex that is known to couple the F-actin cytoskeleton to the nuclear envelope. We demonstrated that fascin, which is predominantly associated with peripheral F-actin rich filopodia, binds directly to Nesprin-2 at the nuclear envelope in a range of cell types. Depleting fascin or specifically blocking the fascin-Nesprin-2 complex leads to defects in nuclear polarization, movement and cell invasion. These studies reveal a novel role for an F-actin bundling protein in control of nuclear plasticity and underline the importance of defining nuclear-associated roles for F-actin binding proteins in future.
Keywords: Fascin; Nesprin-2; actin; cell migration; nuclear deformation; nuclear movement.
Figures
Erratum for
- Extra View to: Jayo A, Malboubi M, Antoku S, Chang W, Ortiz-Zapater E, Groen C, Pfisterer K, Tootle T, Charras G, Gundersen GG, Parsons M. Fascin Regulates Nuclear Movement and Deformation in Migrating Cells. Dev Cell 2016; 38:371–83. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2016.07.021
Similar articles
-
Fascin Regulates Nuclear Movement and Deformation in Migrating Cells.Dev Cell. 2016 Aug 22;38(4):371-83. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.07.021. Dev Cell. 2016. PMID: 27554857 Free PMC article.
-
Nesprin-1 and nesprin-2 regulate endothelial cell shape and migration.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2014 Jul;71(7):423-34. doi: 10.1002/cm.21182. Epub 2014 Jun 25. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2014. PMID: 24931616
-
Reinforcing the LINC complex connection to actin filaments: the role of FHOD1 in TAN line formation and nuclear movement.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(14):2200-5. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1053665. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 26083340 Free PMC article.
-
Nesprin-3: a versatile connector between the nucleus and the cytoskeleton.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Dec;39(6):1719-24. doi: 10.1042/BST20110669. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 22103514 Review.
-
Fascin in Cell Migration: More Than an Actin Bundling Protein.Biology (Basel). 2020 Nov 17;9(11):403. doi: 10.3390/biology9110403. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33212856 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interkinetic nuclear movements promote apical expansion in pseudostratified epithelia at the expense of apicobasal elongation.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Dec 23;15(12):e1007171. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007171. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 31869321 Free PMC article.
-
Nesprin proteins: bridging nuclear envelope dynamics to muscular dysfunction.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Apr 2;22(1):208. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01593-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38566066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Severe ACTA1-related nemaline myopathy: intranuclear rods, cytoplasmic bodies, and enlarged perinuclear space as characteristic pathological features on muscle biopsies.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022 Jul 9;10(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s40478-022-01400-0. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022. PMID: 35810298 Free PMC article.
-
Much More Than a Scaffold: Cytoskeletal Proteins in Neurological Disorders.Cells. 2020 Feb 4;9(2):358. doi: 10.3390/cells9020358. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32033020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mena regulates nesprin-2 to control actin-nuclear lamina associations, trans-nuclear membrane signalling and gene expression.Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 23;14(1):1602. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37021-x. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36959177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crisp M, Liu Q, Roux K, Rattner JB, Shanahan C, Burke B, Stahl PD, Hodzic D. Coupling of the nucleus and cytoplasm: role of the LINC complex. J Cell Biol 2006; 172:41-53; PMID:16380439; http://dx.doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200509124 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Khatau SB, Hale CM, Stewart-Hutchinson PJ, Patel MS, Stewart CL, Searson PC, Hodzic D, Wirtz D. A perinuclear actin cap regulates nuclear shape. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009; 106:19017-22; PMID:19850871; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0908686106 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chambliss AB, Khatau SB, Erdenberger N, Robinson DK, Hodzic D, Longmore GD, Wirtz D. The LINC-anchored actin cap connects the extracellular milieu to the nucleus for ultrafast mechanotransduction. Sci Rep 2013; 3:1087; PMID:23336069; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/srep01087 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim DI, Birendra KC, Roux KJ. Making the LINC: SUN and KASH protein interactions. Biol Chem 2015; 396:295-310; PMID:25720065; http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2014-0267 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rajgor D, Shanahan CM. Nesprins: from the nuclear envelope and beyond. Expert Rev Mol Med 2013; 15:e5; PMID:23830188; http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/erm.2013.6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
