Prognostic impact of CD73 and A2A adenosine receptor expression in non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 28060732
- PMCID: PMC5352437
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14434
Prognostic impact of CD73 and A2A adenosine receptor expression in non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
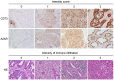
In immune cells, CD73 dephosphorylates and converts extracellular AMP into adenosine, which binds the A2A adenosine receptor (A2AR). Blockade of this interaction, which induces an immunosuppressed niche in the tumor microenvironment, represents a potential novel treatment strategy. The clinical significance of CD73 and A2AR expression in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), however, has yet to be thoroughly investigated. Here we evaluated CD73 and A2AR protein expression levels using immunohistochemistry in tissue microarrays containing 642 resected NSCLC specimens. Furthermore, we compared the expression profiles of 133 paired primary tumors and lymph node metastases. CD73 and A2AR expression levels were significantly higher in females than in males, in never smokers than in ever smokers, and in adenocarcinomas than in squamous cell carcinomas. Among adenocarcinomas, significantly higher CD73 and A2AR expression was observed in TTF-1-positive and mutant EGFR-positive tumors than in their counterparts. Compared with CD73, A2AR expression was more inconsistent between primary tumors and lymph node metastases. Among NSCLC patients, high CD73 expression was an independent indicator of poor prognosis in multivariate Cox regression analyses for overall survival [hazard ratio (HR), 2.18; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.38-3.46] and recurrence-free survival (HR, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.42-2.95). In contrast, high A2AR expression was an independent predictor of favorable prognosis for overall survival (HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.50-0.98) and recurrence-free survival (HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.56-0.97). Together, these findings indicate that CD73 and A2AR have opposing prognostic effects, although cases involving CD73 or A2AR expression share some clinicopathological features.
Keywords: A2AR; CD73; adenosine; non-small-cell lung cancer; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim DW, Felip E, Pérez-Gracia JL, Han JY, Molina J, Kim JH, Arvis CD, Ahn MJ, Majem M, Fidler MJ, de Castro G, Jr, et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;387:1540–1550. - PubMed
-
- Fehrenbacher L, Spira A, Ballinger M, Kowanetz M, Vansteenkiste J, Mazieres J, Park K, Smith D, Artal-Cortes A, Lewanski C, Braiteh F, Waterkamp D, He P, et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel for patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (POPLAR): a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;387:1837–1846. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

