Elevated UHRF1 expression contributes to poor prognosis by promoting cell proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 28060737
- PMCID: PMC5354676
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14446
Elevated UHRF1 expression contributes to poor prognosis by promoting cell proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
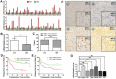
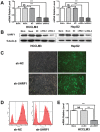
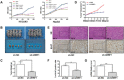
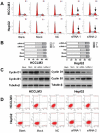
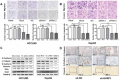
Ubiquitin-like with plant homeodomain and ring finger domains, 1 (UHRF1) is overexpressed in a variety of tumor tissues and is negatively correlated with prognosis of patients with cancers, yet so far, a comprehensive study of UHRF1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has not been conducted. The present study was designed to explore the expression of UHRF1, associated clinical implications, and its possible functions in HCC. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemical staining were used to detect UHRF1 expression in HCC specimens including cancerous and noncancerous tissues. Associations of UHRF1 expression with demographic and clinicopathologic features in HCC were analyzed, and the effects of RNA interference of UHRF1 on cell proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, and migration were investigated in vitro and in vivo. UHRF1 mRNA and protein expression were both upregulated and negatively correlated with prognosis in HCC patients. Furthermore, inhibition of proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression were observed in vitro and in vivo after UHRF1 knockdown, moreover, G2/M arrest was detected in HCC cells. In conclusion, elevated UHRF1 expression contributes to poor prognosis by promoting cell proliferation and metastasis in HCC.
Keywords: HCC; UHRF1; invasion; prognosis; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of brachyury contributes to tumor metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 14;33(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13046-014-0105-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25499255 Free PMC article.
-
FoxM1 overexpression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 7;21(1):196-213. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i1.196. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25574092 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated expression of UHRF1 predicts unfavorable prognosis for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Aug 1;8(8):9416-21. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26464697 Free PMC article.
-
UHRF1: The key regulator of epigenetics and molecular target for cancer therapeutics.Tumour Biol. 2017 Feb;39(2):1010428317692205. doi: 10.1177/1010428317692205. Tumour Biol. 2017. PMID: 28218043 Review.
-
Role of UHRF1 in malignancy and its function as a therapeutic target for molecular docking towards the SRA domain.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019 Sep;114:105558. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.06.006. Epub 2019 Jun 22. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31238111 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals the Role of UHRF1-Mediated DNA Methylation and Immune Infiltration in Renal Cell Carcinoma.J Oncol. 2022 May 23;2022:3842547. doi: 10.1155/2022/3842547. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35656341 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of UHRF1 promotes silencing of tumor suppressor genes and predicts outcome in hepatoblastoma.Clin Epigenetics. 2018 Mar 2;10:27. doi: 10.1186/s13148-018-0462-7. eCollection 2018. Clin Epigenetics. 2018. PMID: 29507645 Free PMC article.
-
A Tox21 Approach to Altered Epigenetic Landscapes: Assessing Epigenetic Toxicity Pathways Leading to Altered Gene Expression and Oncogenic Transformation In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 1;18(6):1179. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061179. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28587163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The epigenetic integrator UHRF1: on the road to become a universal biomarker for cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 24;8(31):51946-51962. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17393. eCollection 2017 Aug 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28881702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ZNF479 downregulates metallothionein-1 expression by regulating ASH2L and DNMT1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2019 May 28;10(6):408. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1651-9. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31138789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
-
- Clark T, Maximin S, Meier J, Pokharel S, Bhargava P. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Review of Epidemiology, Screening, Imaging Diagnosis, Response Assessment, and Treatment. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2015;44:479–86. - PubMed
-
- Liang B, Jia C, Huang Y, He H, Li J, Liao H, Liu X, Liu X, Bai X, Yang D. TPX2 Level Correlates with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis, and EMT. Dig Dis Sci. 2015;60:2360–72. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

