Enhanced Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Umbilical Cord Wharton's Jelly Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells by GSK-3 Inhibitors
- PMID: 28060847
- PMCID: PMC5217863
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168059
Enhanced Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Umbilical Cord Wharton's Jelly Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells by GSK-3 Inhibitors
Abstract
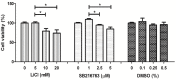
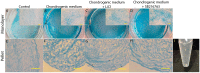
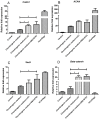
Articular cartilage is an avascular, alymphatic, and aneural system with very low regeneration potential because of its limited capacity for self-repair. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are the preferred choice for cell-based therapies. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) inhibitors are compounds that can induce the Wnt signaling pathway, which is involved in chondrogenesis and cartilage development. Here, we investigated the influence of lithium chloride (LiCl) and SB216763 synergistically with TGF-β3 on chondrogenic differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells derived from Wharton's jelly tissue (hWJ-MSCs). hWJ-MSCs were cultured and chondrogenic differentiation was induced in monolayer and pellet experiments using chondrogenic medium, chondrogenic medium supplemented with LiCl, or SB216763 for 4 weeks. After in vitro differentiation, cultured cells were examined for the expression of Sox9, ACAN, Col2a1, and β-catenin markers. Glycosaminoglycan (GAG) accumulation was also examined by Alcian blue staining. The results indicated that SB216763 was more effective than LiCl as evidenced by a higher up-regulation of the expression of cartilage-specific markers, including Sox9, ACAN, Col2a1 as well as GAG accumulation. Moreover, collagen type II expression was strongly observed in cells cultured in the chondrogenic medium + SB216763 as evidenced by western blot analysis. Both treatments appeared to mediate the Wnt signaling pathway by up-regulating β-catenin gene expression. Further analyses showed that all treatments suppressed the progression of chondrocyte hypertrophy, determined by decreased expression of Col10a1 and Runx2. These results indicate that LiCl and SB216763 are potential candidates for further in vivo therapeutic trials and would be of great importance for cartilage regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was partly supported by the Bangkok Stem Cell Co., Ltd. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products to declare. This does not alter our adherence to all the PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials, as detailed online in the guide for authors.
Figures





References
-
- Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999; 284(5411): 143–147. - PubMed
-
- Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, Huang J, Futrell JW, Katz AJ, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tis Eng. 2001; 7: 211–228. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

