A Comparison of a Machine Learning Model with EuroSCORE II in Predicting Mortality after Elective Cardiac Surgery: A Decision Curve Analysis
- PMID: 28060903
- PMCID: PMC5218502
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169772
A Comparison of a Machine Learning Model with EuroSCORE II in Predicting Mortality after Elective Cardiac Surgery: A Decision Curve Analysis
Abstract
Background: The benefits of cardiac surgery are sometimes difficult to predict and the decision to operate on a given individual is complex. Machine Learning and Decision Curve Analysis (DCA) are recent methods developed to create and evaluate prediction models.
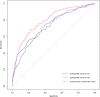
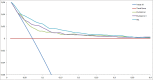
Methods and finding: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using a prospective collected database from December 2005 to December 2012, from a cardiac surgical center at University Hospital. The different models of prediction of mortality in-hospital after elective cardiac surgery, including EuroSCORE II, a logistic regression model and a machine learning model, were compared by ROC and DCA. Of the 6,520 patients having elective cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass, 6.3% died. Mean age was 63.4 years old (standard deviation 14.4), and mean EuroSCORE II was 3.7 (4.8) %. The area under ROC curve (IC95%) for the machine learning model (0.795 (0.755-0.834)) was significantly higher than EuroSCORE II or the logistic regression model (respectively, 0.737 (0.691-0.783) and 0.742 (0.698-0.785), p < 0.0001). Decision Curve Analysis showed that the machine learning model, in this monocentric study, has a greater benefit whatever the probability threshold.
Conclusions: According to ROC and DCA, machine learning model is more accurate in predicting mortality after elective cardiac surgery than EuroSCORE II. These results confirm the use of machine learning methods in the field of medical prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Authors/Task Force members, Windecker S, Kolh P, Alfonso F, Collet J-P, Cremer J, et al. 2014 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization: The Task Force on Myocardial Revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS)Developed with the special contribution of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). Eur Heart J. 2014;35: 2541–2619. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu278 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nashef SAM, Roques F, Sharples LD, Nilsson J, Smith C, Goldstone AR, et al. EuroSCORE II. Eur J Cardio-Thorac Surg Off J Eur Assoc Cardio-Thorac Surg. 2012;41: 734-744-745. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

