Early Fesoterodine Fumarate Administration Prevents Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity in a Spinal Cord Transected Rat Model
- PMID: 28060912
- PMCID: PMC5217950
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169694
Early Fesoterodine Fumarate Administration Prevents Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity in a Spinal Cord Transected Rat Model
Abstract
Background: In spinal cord injury, onset of detrusor overactivity (DO) is detrimental for quality of life (incontinence) and renal risk. Prevention has only been achieved with complex sophisticated electrical neuromodulation techniques.
Purpose: To assess the efficacy of early fesoterodine fumarate (FF) administration in preventing bladder overactivity in a spinal cord transected (SCT) rat model.
Methods: 33 Sprague-Dawley rats were allocated to 6 groups-Group 1: 3 normal controls; Group 2: 6 SCT controls; Group 3: 6 SCT rats + FF 0.18 mg/kg/d; Group 4: 6 SCT rats + FF 0.12 mg/kg/d; Group 5: 6 SCT rats + FF 0.18 mg/kg/d + 72-h wash-out period; Group 6: 6 SCT rats + FF 0.12 mg/kg/d + 72-h wash-out period. SCT was performed at T10. FF was continuously administered. Cystometry was undertaken 6 weeks after SCT in awake rats recording intermicturition pressure (IMP), baseline pressure, threshold pressure (Pthres) and maximum pressure (Pmax). Normal controls and SCT controls were initially compared using the Mann-Whitney U tests in order to confirm the SCT effect on cystometric parameters. The comparisons in cystometric and metabolic cage parameters between SCT controls and treated rats were done using post-hoc Dunn's tests for Kruskal-Wallis analysis. Statistical testing was conducted at the two-tailed α-level of 0.05.
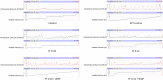
Results: Pressure parameters were significantly higher in SCT control group compared to normal controls. Six weeks after SCT, IMP was significantly lower in low dose treated group than in SCT controls. Pmax was significantly lower in 3 treated groups compared to SCT controls. Pthres was significantly lower in full time treated groups than in SCT controls.
Conclusion: Early administration of FF modulates bladder overactivity in a SCT rat model. Whereas short-term prevention has been demonstrated, the long-term should be further analyzed. Clinical application of these results should confirm this finding through randomized research protocols.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Corcos reports other from Astellas, other from Pfizer, other from Allergan, during the conduct of the study. The Work Under Consideration for Publication: Astellas – adboard member; Pfizer – adboard member; Allergan – adboard member. Dr. Campeau reports other from Pfizer, during the conduct of the study. The Work Under Consideration for Publication: Pfizer - Consultant, Investigator initiated trial. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of oxybutynin transdermal system in spinal cord injury patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity and incontinence: an open-label, dose-titration study.Urology. 2009 Oct;74(4):741-5. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2009.05.008. Epub 2009 Jul 22. Urology. 2009. PMID: 19628264
-
Renal deterioration after spinal cord injury is associated with length of detrusor contractions during cystometry-A study with a median of 41 years follow-up.Neurourol Urodyn. 2017 Aug;36(6):1607-1615. doi: 10.1002/nau.23163. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017. PMID: 27813141
-
Efficacy of fesoterodine fumarate (8 mg) in neurogenic detrusor overactivity due to spinal cord lesion or multiple sclerosis: A prospective study.Neurourol Urodyn. 2021 Nov;40(8):2026-2033. doi: 10.1002/nau.24790. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Neurourol Urodyn. 2021. PMID: 34498773
-
Meta-analysis of botulinum toxin A detrusor injections in the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity after spinal cord injury.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013 Aug;94(8):1473-81. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2013.04.011. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013. PMID: 23632286 Review.
-
Mechanisms of action of botulinum neurotoxins, β3-adrenergic receptor agonists, and PDE5 inhibitors in modulating detrusor function in overactive bladders: ICI-RS 2011.Neurourol Urodyn. 2012 Mar;31(3):300-8. doi: 10.1002/nau.21246. Epub 2012 Jan 24. Neurourol Urodyn. 2012. PMID: 22275187 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug Repurposing for Spinal Cord Injury: Progress Towards Therapeutic Intervention for Primary Factors and Secondary Complications.Pharmaceut Med. 2023 Nov;37(6):463-490. doi: 10.1007/s40290-023-00499-3. Epub 2023 Sep 12. Pharmaceut Med. 2023. PMID: 37698762 Review.
References
-
- Nambiar A, Lucas M. Chapter 4: Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (OAB) and neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO). Neurourol. Urodyn. 2014; 33 Suppl 3: S21–S25. - PubMed
-
- François B, Vacher P, Roustan J, Salle JY, Vidal J, Moreau JJ, et al. Intrathecal baclofen after traumatic brain injury: early treatment using a new technique to prevent spasticity. J. Trauma 2001; 50: 158–161. - PubMed
-
- Salinas FA, Lugo LH, García HI. Efficacy of early treatment with carbamazepine in prevention of neuropathic pain in patients with spinal cord injury. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Assoc. Acad. Physiatr. 2012; 91: 1020–1027. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

