Acute genetic ablation of pendrin lowers blood pressure in mice
- PMID: 28064162
- PMCID: PMC5837383
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfw393
Acute genetic ablation of pendrin lowers blood pressure in mice
Abstract
Background: Pendrin, the chloride/bicarbonate exchanger of β-intercalated cells of the renal connecting tubule and the collecting duct, plays a key role in NaCl reabsorption by the distal nephron. Therefore, pendrin may be important for the control of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure.
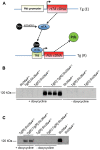
Methods: Here, we have used a genetic mouse model in which the expression of pendrin can be switched-on in vivo by the administration of doxycycline. Pendrin can also be rapidly removed when doxycycline administration is discontinued. Therefore, our genetic strategy allows us to test selectively the acute effects of loss of pendrin function.
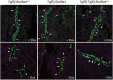
Results: We show that acute loss of pendrin leads to a significant decrease of blood pressure. In addition, acute ablation of pendrin did not alter significantly the acid-base status or blood K + concentration.
Conclusion: By using a transgenic mouse model, avoiding off-target effects related to pharmacological compounds, this study suggests that pendrin could be a novel target to treat hypertension.
Keywords: chloride; diuretics; hypertension; intercalated cells; pendrin.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA. All rights reserved.
Figures

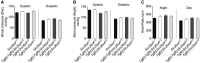
References
-
- Scott DA, Wang R, Kreman TM. et al. The Pendred syndrome gene encodes a chloride-iodide transport protein. Nat Genet 1999; 21: 440–443 - PubMed
-
- Pendred V. Deaf-mutism and goitre. Lancet 1896; 148: 532
-
- Quentin F, Chambrey R, Trinh-Trang-Tan MM. et al. The Cl-/ exchanger pendrin in the rat kidney is regulated in response to chronic alterations in chloride balance. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2004; 287: F1179–F1188 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

