Childhood epilepsies: What should a pediatrician know?
- PMID: 28064325
- PMCID: PMC5726831
- DOI: 10.17712/nsj.2017.1.20160244
Childhood epilepsies: What should a pediatrician know?
Abstract
Seizures in children are among the most common neurological disorders. A pediatrician should know how to approach a child who presents with a seizure. This review will focus on points that are important in the evaluation of children who have experienced seizures. A comprehensive and neurologically focused framework for history taking and a thorough clinical examination are the cornerstones in diagnosing and managing seizures. This article reviews the clinical approach to the diagnosis, investigation, and management of epilepsy in children, excluding neonatal seizures. A pediatrician should also be aware of common epilepsy syndromes that occur in children such as Benign Childhood Epilepsy with Centro-Temporal Spikes, and childhood absence epilepsy.
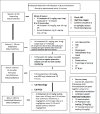
Figures
References
-
- Camfield P, Camfield C. Incidence, prevalence and aetiology of seizures and epilepsy in children. Epileptic Disord. 2015;17:117–123. - PubMed
-
- Kim H, Thurman DJ, Durgin T, Faught E, Helmers S. Estimating Epilepsy Incidence and Prevalence in the US Pediatric Population Using Nationwide Health Insurance Claims Data. J Child Neurol. 2016;31:743–749. - PubMed
-
- Friedman MJ, Sharieff GQ. Seizures in children. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2006;53:257–277. - PubMed
-
- Foy JM, Duncan P, Frankowski B, Kelleher K, Knapp PK, Laraque D, et al. Enhancing pediatric mental health care:algorithms for primary care. Pediatrics. 2010;125:109–125. - PubMed
-
- Vendrame M, Zarowski M, Alexopoulos AV, Wyllie E, Kothare SV, Loddenkemper T. Localization of pediatric seizure semiology. Clin Neurophysiol. 2011;122:1924–1928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
