Glycosaminoglycan levels in dried blood spots of patients with mucopolysaccharidoses and mucolipidoses
- PMID: 28065440
- PMCID: PMC5346460
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2016.12.010
Glycosaminoglycan levels in dried blood spots of patients with mucopolysaccharidoses and mucolipidoses
Abstract
Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPSs) and mucolipidoses (ML) are groups of lysosomal storage disorders in which lysosomal hydrolases are deficient leading to accumulation of undegraded glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), throughout the body, subsequently resulting in progressive damage to multiple tissues and organs. Assays using tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) have been established to measure GAGs in serum or plasma from MPS and ML patients, but few studies were performed to determine whether these assays are sufficiently robust to measure GAG levels in dried blood spots (DBS) of patients with MPS and ML.
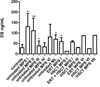
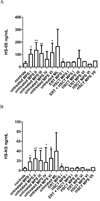
Material and methods: In this study, we evaluated GAG levels in DBS samples from 124 MPS and ML patients (MPS I=16; MPS II=21; MPS III=40; MPS IV=32; MPS VI=10; MPS VII=1; ML=4), and compared them with 115 age-matched controls. Disaccharides were produced from polymer GAGs by digestion with chondroitinase B, heparitinase, and keratanase II. Subsequently, dermatan sulfate (DS), heparan sulfate (HS-0S, HS-NS), and keratan sulfate (mono-sulfated KS, di-sulfated KS, and ratio of di-sulfated KS in total KS) were measured by MS/MS.
Results: Untreated patients with MPS I, II, VI, and ML had higher levels of DS compared to control samples. Untreated patients with MPS I, II, III, VI, and ML had higher levels of HS-0S; and untreated patients with MPS II, III and VI and ML had higher levels of HS-NS. Levels of KS were age dependent, so although levels of both mono-sulfated KS and di-sulfated KS were generally higher in patients, particularly for MPS II and MPS IV, age group numbers were not sufficient to determine significance of such changes. However, the ratio of di-sulfated KS in total KS was significantly higher in all MPS patients younger than 5years old, compared to age-matched controls. MPS I and VI patients treated with HSCT had normal levels of DS, and MPS I, VI, and VII treated with ERT or HSCT had normal levels of HS-0S and HS-NS, indicating that both treatments are effective in decreasing blood GAG levels.
Conclusion: Measurement of GAG levels in DBS is useful for diagnosis and potentially for monitoring the therapeutic efficacy in MPS.
Keywords: Glycosaminoglycans; Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; Mucolipidoses; Mucopolysaccharidoses; Tandem mass spectrometry.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Francyne Kubaski, Yasuyuki Suzuki, Kenji Orii, Roberto Giugliani, Heather J. Church, Robert W. Mason, Vũ Chí Dũng, Can Thi Bich Ngoc, Seiji Yamaguchi, Hironori Kobayashi, Katta M. Girisha, Toshiyuki Fukao, Tadao Orii, and Shunji Tomatsu declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycosaminoglycans analysis in blood and urine of patients with mucopolysaccharidosis.Mol Genet Metab. 2018 Sep;125(1-2):44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2018.04.011. Epub 2018 May 17. Mol Genet Metab. 2018. PMID: 29779903 Free PMC article.
-
Newborn screening for mucopolysaccharidoses: a pilot study of measurement of glycosaminoglycans by tandem mass spectrometry.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2017 Jan;40(1):151-158. doi: 10.1007/s10545-016-9981-6. Epub 2016 Oct 7. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2017. PMID: 27718145 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of disaccharide compositions derived from dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate in mucopolysaccharidoses and mucolipidoses II and III by tandem mass spectrometry.Mol Genet Metab. 2010 Feb;99(2):124-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2009.10.001. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Mol Genet Metab. 2010. PMID: 19932038
-
Newborn screening and diagnosis of mucopolysaccharidoses.Mol Genet Metab. 2013 Sep-Oct;110(1-2):42-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Mol Genet Metab. 2013. PMID: 23860310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycosaminoglycans in mucopolysaccharidoses and other disorders.Adv Clin Chem. 2024;122:1-52. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2024.06.011. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Adv Clin Chem. 2024. PMID: 39111960 Review.
Cited by
-
Fast, sensitive method for trisaccharide biomarker detection in mucopolysaccharidosis type 1.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 27;8(1):3681. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22078-2. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29487322 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosaminoglycans analysis in blood and urine of patients with mucopolysaccharidosis.Mol Genet Metab. 2018 Sep;125(1-2):44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2018.04.011. Epub 2018 May 17. Mol Genet Metab. 2018. PMID: 29779903 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement in time to treatment, but not time to diagnosis, in patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type I.Arch Dis Child. 2021 Jul;106(7):674-679. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2020-319040. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Arch Dis Child. 2021. PMID: 33139350 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous, non-reducing end glycosaminoglycan biomarkers are superior to internal disaccharide glycosaminoglycan biomarkers for newborn screening of mucopolysaccharidoses and GM1 gangliosidosis.Mol Genet Metab. 2023 Sep-Oct;140(1-2):107632. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2023.107632. Epub 2023 Jun 24. Mol Genet Metab. 2023. PMID: 37407323 Free PMC article.
-
Novel human recombinant N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase produced in a glyco-engineered Escherichia coli strain.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 8;10(12):e32555. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32555. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38952373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neufeld Elizabeht, Muenzer Joseph. The Mucopolysaccharidoses, 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2001.
-
- Braulke T, Raas-Rotchschild A, Kornfeld S, Sly WS. I-cell disease, pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy: disorders of lysosomal enzyme phosphorylation, localization. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, Childs B, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, editors. The Metabolic, Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, 8 Ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2001. pp. 3469–3482. assoc. eds. I-cell disease and pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy: disorders of lysosomal enzyme phosphorylation and localization 3469-82.
-
- Wraith JE. Mucopolysaccharidoses and mucolipidoses. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;113:1723–1729. - PubMed
-
- Tomatsu S, Gutierrez MA, Ishimaru T, Peña OM, Montaño AM, Maeda H, Velez-Castrillon S, Nishioka T, Fachel AA, Cooper A, Thornley M, Wraith E, Barrera LA, Laybauer LS, Giugliani R, Schwartz IV, Frenking GS, Beck M, Kircher SG, Paschke E, Yamaguchi S, Ullrich K, Isogai K, Suzuki Y, Orii T, Noguchi A. Heparan sulfate levels in mucopolysaccharidoses and mucolipidoses. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2005;28:743–757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

