Initiation of Quality Control during Poly(A) Translation Requires Site-Specific Ribosome Ubiquitination
- PMID: 28065601
- PMCID: PMC5316413
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.11.039
Initiation of Quality Control during Poly(A) Translation Requires Site-Specific Ribosome Ubiquitination
Abstract
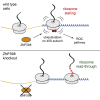
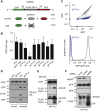
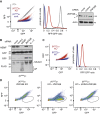
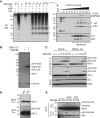
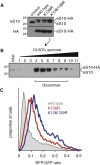
Diverse cellular stressors have been observed to trigger site-specific ubiquitination on several ribosomal proteins. However, the ubiquitin ligases, biochemical consequences, and physiologic pathways linked to these modifications are not known. Here, we show in mammalian cells that the ubiquitin ligase ZNF598 is required for ribosomes to terminally stall during translation of poly(A) sequences. ZNF598-mediated stalling initiated the ribosome-associated quality control (RQC) pathway for degradation of nascent truncated proteins. Biochemical ubiquitination reactions identified two sites of mono-ubiquitination on the 40S protein eS10 as the primary ribosomal target of ZNF598. Cells lacking ZNF598 activity or containing ubiquitination-resistant eS10 ribosomes failed to stall efficiently on poly(A) sequences. In the absence of stalling, read-through of poly(A) produces a poly-lysine tag, which might alter the localization and solubility of the associated protein. Thus, ribosome ubiquitination can modulate translation elongation and impacts co-translational quality control to minimize production of aberrant proteins.
Keywords: nonstop mRNA; poly(A); protein quality control; ribosome stalling; translation; ubiquitination.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

