Mechanisms that determine nanocarrier targeting to healthy versus inflamed lung regions
- PMID: 28065731
- PMCID: PMC5518469
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nano.2016.12.019
Mechanisms that determine nanocarrier targeting to healthy versus inflamed lung regions
Abstract
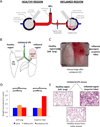
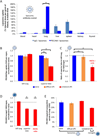
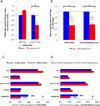
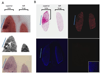
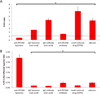
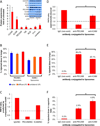
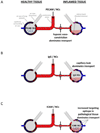
Inflamed organs display marked spatial heterogeneity of inflammation, with patches of inflamed tissue adjacent to healthy tissue. To investigate how nanocarriers (NCs) distribute between such patches, we created a mouse model that recapitulates the spatial heterogeneity of the inflammatory lung disease ARDS. NCs targeting the epitope PECAM strongly accumulated in the lungs, but were shunted away from inflamed lung regions due to hypoxic vasoconstriction (HVC). In contrast, ICAM-targeted NCs, which had lower whole-lung uptake than PECAM/NCs in inflamed lungs, displayed markedly higher NC levels in inflamed regions than PECAM/NCs, due to increased regional ICAM. Regional HVC, epitope expression, and capillary leak were sufficient to predict intra-organ of distribution of NCs, antibodies, and drugs. Importantly, these effects were not observable with traditional spatially-uniform models of ARDS, nor when examining only whole-organ uptake. This study underscores how examining NCs' intra-organ distribution in spatially heterogeneous animal models can guide rational NC design.
Keywords: ARDS; Inflammation; Nano-bio interface; Nanocarriers; Nanoparticle biological interactions; Nanoparticles; Patchy; Spatial heterogeneity; Whole organ distribution.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Kowalski PS, Kuninty PR, Bijlsma KT, Stuart MCA, Leus NGJ, Ruiters MHJ, et al. SAINT-liposome-polycation particles, a new carrier for improved delivery of siRNAs to inflamed endothelial cells. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;89:40–47. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 HL007439/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090697/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL125462/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007586/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 EB016027/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087036/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126874/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007775/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007971/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL121134/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL129665/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007954/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007915/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL130430/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

