Efficacy and tolerability of topical sertaconazole versus topical terbinafine in localized dermatophytosis: A randomized, observer-blind, parallel group study
- PMID: 28066103
- PMCID: PMC5155466
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.194850
Efficacy and tolerability of topical sertaconazole versus topical terbinafine in localized dermatophytosis: A randomized, observer-blind, parallel group study
Abstract
Objective: Epidermal dermatophyte infections most commonly manifest as tinea corporis or tinea cruris. Topical azole antifungals are commonly used in their treatment but literature suggests that most require twice-daily application and provide lower cure rates than the allylamine antifungal terbinafine. We conducted a head-to-head comparison of the effectiveness of the once-daily topical azole, sertaconazole, with terbinafine in these infections.
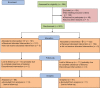
Materials and methods: We conducted a randomized, observer-blind, parallel group study (Clinical Trial Registry India [CTRI]/2014/09/005029) with adult patients of either sex presenting with localized lesions. The clinical diagnosis was confirmed by potassium hydroxide smear microscopy of skin scrapings. After baseline assessment of erythema, scaling, and pruritus, patients applied either of the two study drugs once daily for 2 weeks. If clinical cure was not seen at 2 weeks, but improvement was noted, application was continued for further 2 weeks. Patients deemed to be clinical failure at 2 weeks were switched to oral antifungals.
Results: Overall 88 patients on sertaconazole and 91 on terbinafine were analyzed. At 2 weeks, the clinical cure rates were comparable at 77.27% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 68.52%-86.03%) for sertaconazole and 73.63% (95% CI 64.57%-82.68%) for terbinafine (P = 0.606). Fourteen patients in either group improved and on further treatment showed complete healing by another 2 weeks. The final cure rate at 4 weeks was also comparable at 93.18% (95% CI 88.75%-97.62%) and 89.01% (95% CI 82.59%-95.44%), respectively (P = 0.914). At 2 weeks, 6 (6.82%) sertaconazole and 10 (10.99%) terbinafine recipients were considered as "clinical failure." Tolerability of both preparations was excellent.
Conclusion: Despite the limitations of an observer-blind study without microbiological support, the results suggest that once-daily topical sertaconazole is as effective as terbinafine in localized tinea infections.
Keywords: Antifungal; dermatophytosis; observer-blind; parallel group study; randomized; sertaconazole; terbinafine; tinea.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A randomized, double-blind trial of amorolfine 0.25% cream and sertaconazole 2% cream in limited dermatophytosis.Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2019 May-Jun;85(3):276-281. doi: 10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_907_17. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2019. PMID: 30409926 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Terbinafine Hydrochloride 1% Cream vs. Sertaconazole Nitrate 2% Cream in Tinea Corporis and Tinea Cruris: A Comparative Therapeutic Trial.Indian J Dermatol. 2013 Nov;58(6):457-60. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.119958. Indian J Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 24249898 Free PMC article.
-
Once daily treatment with terbinafine 1% cream (Lamisil) for one week is effective in the treatment of tinea corporis and cruris. A placebo-controlled study.Mycoses. 2001;44(7-8):300-6. Mycoses. 2001. PMID: 11714065 Clinical Trial.
-
Sertaconazole: a review of its use in the management of superficial mycoses in dermatology and gynaecology.Drugs. 2009;69(3):339-59. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200969030-00009. Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19275277 Review.
-
Terbinafine. An update of its use in superficial mycoses.Drugs. 1999 Jul;58(1):179-202. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199958010-00018. Drugs. 1999. PMID: 10439936 Review.
Cited by
-
A Meta-Analysis on the Effectiveness of Sertaconazole 2% Cream Compared with Other Topical Therapies for Seborrheic Dermatitis.J Pers Med. 2022 Sep 19;12(9):1540. doi: 10.3390/jpm12091540. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36143325 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of the efficacy of itraconazole with terbinafine cream versus itraconazole with sertaconazole cream in dermatophytosis: A within person pilot study.Med J Armed Forces India. 2023 Sep-Oct;79(5):526-530. doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2021.07.001. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Med J Armed Forces India. 2023. PMID: 37719899 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of efficacy, safety, and cost-effectiveness of sertaconazole and luliconazole cream in patients with dermatophytoses: A prospective, randomized, open-label study.Perspect Clin Res. 2021 Oct-Dec;12(4):223-228. doi: 10.4103/picr.PICR_24_19. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Perspect Clin Res. 2021. PMID: 34760651 Free PMC article.
-
Newer Topical Treatments in Skin and Nail Dermatophyte Infections.Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018 May-Jun;9(3):149-158. doi: 10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_281_17. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018. PMID: 29854633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Eberconazole vs Sertaconazole in Localised Tinea Infection.Indian J Dermatol. 2021 Sep-Oct;66(5):573. doi: 10.4103/ijd.IJD_893_20. Indian J Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 35068526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pakshir K, Hashemi J. Dermatophytosis in Karaj, Iran. Indian J Dermatol. 2006;51:262–4.
-
- Thomas B. Clear choices in managing epidermal tinea infections. J Fam Pract. 2003;52:850–62. - PubMed
-
- Weinstein A, Berman B. Topical treatment of common superficial tinea infections. Am Fam Physician. 2002;65:2095–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

