Reduced Activity of the Aortic Gamma-Glutamyltransferase Does Not Decrease S-Nitrosoglutathione Induced Vasorelaxation of Rat Aortic Rings
- PMID: 28066263
- PMCID: PMC5168561
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00630
Reduced Activity of the Aortic Gamma-Glutamyltransferase Does Not Decrease S-Nitrosoglutathione Induced Vasorelaxation of Rat Aortic Rings
Abstract
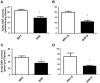
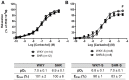
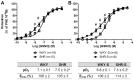
Aims: Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), an enzyme present on the endothelium, is involved in the release of nitric oxide (NO) from S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) and in the GSNO-induced vasodilation. Endogenous GSNO is a physiological storage form of NO in tissues while exogenous GSNO is an interesting candidate for compensating for the decreased NO bioavailability occurring during cardiovascular diseases. We investigated in a rat model of human hypertension, the spontaneous hypertensive rat (SHR), submitted or not to high salt diet, whether a decreased vascular GGT activity modifies the vasorelaxant effect of GSNO. Methods: Thoracic aortic rings isolated from male SHR and Wistar Kyoto rats (WKY) aged 20-22 weeks-submitted or not for 8 weeks to a high salt diet (1% w/v NaCl in drinking water) were pre-constricted with phenylephrine then submitted to concentration-vasorelaxant response curves (maximal response: Emax; pD2) to carbachol or sodium nitroprusside to evaluate endothelial dependent or independent NO-induced vasodilation, or GSNO (exogenous NO vasodilation depending from the endothelial GGT activity). GGT activity was measured using a chromogenic substrate in aortic homogenates. Its role in GSNO-induced relaxation was assessed following inhibition of the enzyme activity (serine-borate complex). That of protein disulfide isomerase (PDI), another redox sensitive enzyme involved in GSNO metabolism, was assessed following inhibition with bacitracin. Results: Aortic GGT activity (18-23 μmol/min/mg of tissue in adult WKY) decreased by 33% in SHR and 45% in SHR with high salt diet. Emax and pD2 for sodium nitroprusside were similar in all groups. Emax for carbachol decreased by -14%, reflecting slight endothelial NO-dependent dysfunction. The GSNO curve was slightly shifted to the left in SHR and in SHR with high salt diet, showing a small enhanced sensitivity to GSNO. Involvements of GGT, as that of PDI, in the GSNO effects were similar in all groups (pD2 for GSNO -0.5 to -1.5 following enzymatic inhibition). Conclusion: Hypertension is associated with a decreased aortic GGT activity without decreasing the vasorelaxant effects of GSNO, whose bioactivity may be supplemented through the alternative enzymatic activity of PDI.
Keywords: NO-dependent vasorelaxation; S-nitrosoglutathione; Spontaneous Hypertensive Rat; aortic ring; gamma-glutamyltransferase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aging and hypertension decrease endothelial NO-related dilating function and gamma-glutamyl transferase activity but not S-nitrosoglutathione-induced aortic vasodilation.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;32(2):134-140. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12347. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29337396
-
Endothelial γ-glutamyltransferase contributes to the vasorelaxant effect of S-nitrosoglutathione in rat aorta.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e43190. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043190. Epub 2012 Sep 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22984412 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress enhances and modulates protein S-nitrosation in smooth muscle cells exposed to S-nitrosoglutathione.Nitric Oxide. 2017 Sep 30;69:10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2017.07.004. Epub 2017 Jul 23. Nitric Oxide. 2017. PMID: 28743484
-
Pre-eclampsia: the Potential of GSNO Reductase Inhibitors.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2017 Mar;19(3):20. doi: 10.1007/s11906-017-0717-2. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2017. PMID: 28271419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Mini Review of S-Nitrosoglutathione Loaded Nano/Micro-Formulation Strategies.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Jan 4;13(2):224. doi: 10.3390/nano13020224. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36677977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GSNO as a Modulator of Vascular Tone in Human Saphenous Veins: Potential Implications for Graft Spasm.Life (Basel). 2025 Jul 19;15(7):1139. doi: 10.3390/life15071139. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40724641 Free PMC article.
-
Association between serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and early-onset coronary artery disease: a retrospective case-control study.Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2289606. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2289606. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 38061693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagnost T., Berthelot A., Bouhaddi M., Laurant P., André C., Guillaume Y., et al. . (2008). Treatment with the arginase inhibitor N(omega)-hydroxy-nor-L-arginine improves vascular function and lowers blood pressure in adult spontaneously hypertensive rat. J. Hypertens 26, 1110–1118. 10.1097/HJH.0b013e3282fcc357 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bauer J. A., Fung H. L. (1991). Differential hemodynamic effects and tolerance properties of nitroglycerin and an S-nitrosothiol in experimental heart failure. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 256, 249–254. - PubMed
-
- Boulanger C. M., Morrison K. J., Vanhoutte P. M. (1994). Mediation by M3-muscarinic receptors of both endothelium-dependent contraction and relaxation to acetylcholine in the aorta of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 112, 519–524. 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13104.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

