Characterization and Antibacterial Potential of Lactic Acid Bacterium Pediococcus pentosaceus 4I1 Isolated from Freshwater Fish Zacco koreanus
- PMID: 28066360
- PMCID: PMC5167689
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.02037
Characterization and Antibacterial Potential of Lactic Acid Bacterium Pediococcus pentosaceus 4I1 Isolated from Freshwater Fish Zacco koreanus
Abstract
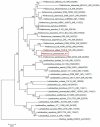
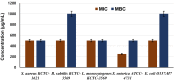
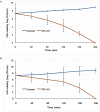
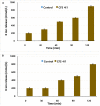
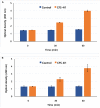
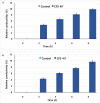
This study was undertaken to characterize a lactic acid bacterium 4I1, isolated from the freshwater fish, Zacco koreanus. Morphological, biochemical, and molecular characterization of 4I1 revealed it to be Pediococcus pentosaceus 4I1. The cell free supernatant (CFS) of P. pentosaceus 4I1 exhibited significant (p < 0.05) antibacterial effects (inhibition zone diameters: 16.5-20.4 mm) against tested foodborne pathogenic bacteria with MIC and MBC values of 250-500 and 500-1,000 μg/mL, respectively. Further, antibacterial action of CFS of P. pentosaceus 4I1 against two selected bacteria Staphylococcus aureus KCTC-1621 and Escherichia coli O157:H7 was determined in subsequent assays. The CFS of P. pentosaceus 4I1 revealed its antibacterial action against S. aureus KCTC-1621 and E. coli O157:H7 on membrane integrity as confirmed by a reduction in cell viability, increased potassium ion release (900 and 800 mmol/L), reduced absorption at 260-nm (3.99 and 3.77 OD), and increased relative electrical conductivity (9.9 and 9.7%), respectively. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis of the CFS of P. pentosaceus 4I1 resulted in the identification of seven major compounds, which included amino acids, fatty acids and organic acids. Scanning electron microscopic-based morphological analysis further confirmed the antibacterial effect of CFS of P. pentosaceus 4I1 against S. aureus KCTC-1621 and E. coli O157:H7. In addition, the CFS of P. Pentosaceus 4I1 displayed potent inhibitory effects on biofilms formation by S. aureus KCTC-1621 and E. coli O157:H7. The study indicates the CFS of P. pentosaceus 4I1 offers an alternative means of controlling foodborne pathogens.
Keywords: Pediococcus pentosaceus 4I1; Zacco koreanus; antimicrobial action; cell free supernatant; foodborne pathogens.
Figures


References
-
- Amenu D. (2013). Antimicrobial activity of lactic acid bacteria isolated from “Ergo”, Ethiopian traditional fermented milk. Curr. Res. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1 278–284.
-
- Ammor S., Tauveron G., Dufour E., Chevallier I. (2006). Antibacterial activity of lactic acid bacteria against spoilage and pathogenic bacteria isolated from the same meat small-scale facility: 1—screening and characterization of the antibacterial compounds. Food Control 17 454–461. 10.1016/j.foodcont.2005.02.007 - DOI
-
- Anas M., Eddine H. J., Mebrouk K. (2008). Antimicrobial activity of Lactobacillus species isolated from Algerian raw goat’s milk against Staphylococcus aureus. World J. Dairy Food Sci. 3 39–49.
-
- Aoudia N., Rieu A., Briandet R., Deschamps J., Chluba J., Jego G., et al. (2016). Biofilms of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus fermentum: effect on stress responses, antagonistic effects on pathogen growth and immunomodulatory properties. Food Microbiol. 53 51–59. 10.1016/j.fm.2015.04.009 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

