Human C1q Induces Apoptosis in an Ovarian Cancer Cell Line via Tumor Necrosis Factor Pathway
- PMID: 28066412
- PMCID: PMC5174108
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00599
Human C1q Induces Apoptosis in an Ovarian Cancer Cell Line via Tumor Necrosis Factor Pathway
Abstract
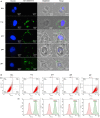
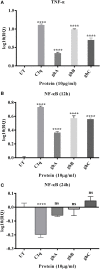
Complement protein C1q is the first recognition subcomponent of the complement classical pathway that plays a vital role in the clearance of immune complexes, pathogens, and apoptotic cells. C1q also has a homeostatic role involving immune and non-immune cells; these functions not necessarily involve complement activation. Recently, C1q has been shown to be expressed locally in the microenvironment of a range of human malignant tumors, where it can promote cancer cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation, without involving complement activation. C1q has been shown to be present in the ascitic fluid formed during ovarian cancers. In this study, we have examined the effects of human C1q and its globular domain on an ovarian cancer cell line, SKOV3. We show that C1q and the recombinant globular head modules induce apoptosis in SKOV3 cells in a time-dependent manner. C1q expression was not detectable in the SKOV3 cells. Exogenous treatment with C1q and globular head modules at the concentration of 10 µg/ml induced apoptosis in approximately 55% cells, as revealed by immunofluorescence microscopy and FACS. The qPCR and caspase analysis suggested that C1q and globular head modules activated tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and upregulated Fas. The genes of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), RICTOR, and RAPTOR survival pathways, which are often overexpressed in majority of the cancers, were significantly downregulated within few hours of the treatment of SKOV3 cells with C1q and globular head modules. In conclusion, C1q, via its globular domain, induced apoptosis in an ovarian cancer cell line SKOV3 via TNF-α induced apoptosis pathway involving upregulation of Bax and Fas. This study highlights a potentially protective role of C1q in certain cancers.
Keywords: C1q; TNF; apoptosis; complement; mTOR; ovarian cancer.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Complement Protein C1q Binds to Hyaluronic Acid in the Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Microenvironment and Promotes Tumor Growth.Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 20;8:1559. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01559. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29209316 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in the understanding of the structure-function relationships of the globular head regions of C1q.Immunobiology. 2002 Sep;205(4-5):355-64. doi: 10.1078/0171-2985-00138. Immunobiology. 2002. PMID: 12395999 Review.
-
Complement Protein C1q Interacts with DC-SIGN via Its Globular Domain and Thus May Interfere with HIV-1 Transmission.Front Immunol. 2016 Dec 22;7:600. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00600. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 28066413 Free PMC article.
-
Direct binding of C1q to apoptotic cells and cell blebs induces complement activation.Eur J Immunol. 2002 Jun;32(6):1726-36. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200206)32:6<1726::AID-IMMU1726>3.0.CO;2-R. Eur J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12115656
-
The non-classical functions of the classical complement pathway recognition subcomponent C1q.Immunol Lett. 2010 Jul 8;131(2):139-50. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2010.03.012. Epub 2010 Apr 8. Immunol Lett. 2010. PMID: 20381531 Review.
Cited by
-
Causal relationship between complement C1QB and colorectal cancer: a drug target Mendelian randomization study.Front Genet. 2024 Jul 23;15:1403509. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1403509. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39109334 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Implications of the Complement Protein C1q in Gliomas.Front Immunol. 2019 Oct 10;10:2366. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02366. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31649675 Free PMC article.
-
Is the A-Chain the Engine That Drives the Diversity of C1q Functions? Revisiting Its Unique Structure.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 5;9:162. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00162. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29459870 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Implications of the Complement Protein C1Q and Its Correlation with Immune Infiltrates in Osteosarcoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Mar 5;14:1737-1751. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S295063. eCollection 2021. Onco Targets Ther. 2021. PMID: 33707956 Free PMC article.
-
Cigarette smoke-induced reduction of C1q promotes emphysema.JCI Insight. 2019 May 21;5(13):e124317. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.124317. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 31112138 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

