Hall of Fame among Pro-inflammatory Cytokines: Interleukin-6 Gene and Its Transcriptional Regulation Mechanisms
- PMID: 28066415
- PMCID: PMC5165036
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00604
Hall of Fame among Pro-inflammatory Cytokines: Interleukin-6 Gene and Its Transcriptional Regulation Mechanisms
Abstract
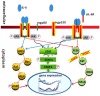
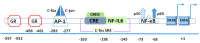
Pro-inflammatory cytokines that are generated by immune system cells and mediate many kinds of immune responses are kinds of endogenous polypeptides. They are also the effectors of the autoimmune system. It is generally accepted that interleukin (IL)-4, IL-6, IL-9, IL-17, and tumor necrosis factor-α are pro-inflammatory cytokines; however, IL-6 becomes a protagonist among them since it predominately induces pro-inflammatory signaling and regulates massive cellular processes. It has been ascertained that IL-6 is associated with a large number of diseases with inflammatory background, such as anemia of chronic diseases, angiogenesis acute-phase response, bone metabolism, cartilage metabolism, and multiple cancers. Despite great progress in the relative field, the targeted regulation of IL-6 response for therapeutic benefits remains incompletely to be understood. Therefore, it is conceivable that understanding mechanisms of IL-6 from the perspective of gene regulation can better facilitate to determine the pathogenesis of the disease, providing more solid scientific basis for clinical treatment translation. In this review, we summarize the candidate genes that have been implicated in clinical target therapy from the perspective of gene transcription regulation.
Keywords: interleukin-6; interleukin-6 gene; pro-inflammatory cytokines; signaling pathway; transcriptional regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pro-inflammatory cytokines negatively regulate PPARγ mediated gene expression in both human and murine macrophages via multiple mechanisms.Immunobiology. 2013 Nov;218(11):1336-44. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.06.011. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 23870825
-
Targeting interleukin-6 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases and cancers.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Feb;141(2):125-39. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.09.004. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24076269 Review.
-
Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor: effector cytokines in autoimmune diseases.Semin Immunol. 1992 Jun;4(3):133-45. Semin Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1320950 Review.
-
Protection against cartilage and bone destruction by systemic interleukin-4 treatment in established murine type II collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Res. 1999;1(1):81-91. doi: 10.1186/ar14. Epub 1999 Oct 26. Arthritis Res. 1999. PMID: 11056663 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory properties of human serum immunoglobulin A: anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory activities in human monocytes and peripheral blood mononuclear cells.Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Jun;140(3):478-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02779.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15932509 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
ZC3H11A loss of function enhances NF-κB signaling through defective IκBα protein expression.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 9;13:1002823. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1002823. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36439101 Free PMC article.
-
Concomitant medications and immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy for cancer: causation or association?Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021 Jan 2;17(1):55-61. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1769398. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021. PMID: 32574106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and Development of Therapeutics for COVID-19.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2021 Mar 3:arXiv:2103.02723v3. ArXiv. 2021. Update in: mSystems. 2021 Dec 21;6(6):e0023321. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00233-21. PMID: 33688554 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
USP24 induces IL-6 in tumor-associated microenvironment by stabilizing p300 and β-TrCP and promotes cancer malignancy.Nat Commun. 2018 Sep 28;9(1):3996. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06178-1. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30266897 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis on Gut Barrier Function, Proinflammatory Response, ROS Production and Pathogen Inhibition Properties in IPEC-J2-Escherichia coli/Salmonella Typhimurium Co-Culture.Microorganisms. 2022 Apr 29;10(5):936. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10050936. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35630380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira S, Hirano T, Taga T, Kishimoto T. Biology of multifunctional cytokines: IL 6 and related molecules (IL 1 and TNF). FASEB J (1990) 4:2860–7. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

