A new method for assessing the risk of infectious disease outbreak
- PMID: 28067258
- PMCID: PMC5220355
- DOI: 10.1038/srep40084
A new method for assessing the risk of infectious disease outbreak
Abstract
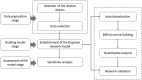
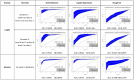
Over the past few years, emergent threats posed by infectious diseases and bioterrorism have become public health concerns that have increased the need for prompt disease outbreak warnings. In most of the existing disease surveillance systems, disease outbreak risk is assessed by the detection of disease outbreaks. However, this is a retrospective approach that impacts the timeliness of the warning. Some disease surveillance systems can predict the probabilities of infectious disease outbreaks in advance by determining the relationship between a disease outbreak and the risk factors. However, this process depends on the availability of risk factor data. In this article, we propose a Bayesian belief network (BBN) method to assess disease outbreak risks at different spatial scales based on cases or virus detection rates. Our experimental results show that this method is more accurate than traditional methods and can make uncertainty estimates, even when some data are unavailable.
Figures




References
-
- Li L. T. et al. A patient-centered early warning system to prevent readmission after colorectal surgery: A national consensus using the Delphi method. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 216, 210–216 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Wagner M. M. et al. The emerging science of very early detection of disease outbreaks. J. Public Health Manag. Pract. 7, 51–59 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Waidyanatha N. Towards a typology of integrated functional early warning systems. International Journal of Criti. 6, 31–51 (2010).
-
- Faensen D. et al. SurvNet@ RKI-a multistate electronic reporting system for communicable diseases. EuroSurveill. 11, 100–3 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

