Nanocaged platforms: modification, drug delivery and nanotoxicity. Opening synthetic cages to release the tiger
- PMID: 28067384
- PMCID: PMC5300024
- DOI: 10.1039/c6nr07315h
Nanocaged platforms: modification, drug delivery and nanotoxicity. Opening synthetic cages to release the tiger
Abstract
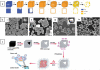
Nanocages (NCs) have emerged as a new class of drug-carriers, with a wide range of possibilities in multi-modality medical treatments and theranostics. Nanocages can overcome such limitations as high toxicity caused by anti-cancer chemotherapy or by the nanocarrier itself, due to their unique characteristics. These properties consist of: (1) a high loading-capacity (spacious interior); (2) a porous structure (analogous to openings between the bars of the cage); (3) enabling smart release (a key to unlock the cage); and (4) a low likelihood of unfavorable immune responses (the outside of the cage is safe). In this review, we cover different classes of NC structures such as virus-like particles (VLPs), protein NCs, DNA NCs, supramolecular nanosystems, hybrid metal-organic NCs, gold NCs, carbon-based NCs and silica NCs. Moreover, NC-assisted drug delivery including modification methods, drug immobilization, active targeting, and stimulus-responsive release mechanisms are discussed, highlighting the advantages, disadvantages and challenges. Finally, translation of NCs into clinical applications, and an up-to-date assessment of the nanotoxicology considerations of NCs are presented.
Figures







References
-
- Sahandi Zangabad P, Khodabakhshi F, Simchi A, Kokabi AH. International Journal of Fatigue. 2016;87:266–278.
-
- Mahmoudi N, Simchi A. Materials Science and Engineering: C. 2017;70:121–131. - PubMed
-
- Mirkin CA, Meade TJ, Petrosko SH, Stegh AH. Nanotechnology-Based Precision Tools for the Detection and Treatment of Cancer. Springer; 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

