Marine Oil Supplements for Arthritis Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials
- PMID: 28067815
- PMCID: PMC5295086
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9010042
Marine Oil Supplements for Arthritis Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials
Abstract
Arthritis patients often take fish oil supplements to alleviate symptoms, but limited evidence exists regarding their efficacy. The objective was to evaluate whether marine oil supplements reduce pain and/or improve other clinical outcomes in patients with arthritis. Six databases were searched systematically (24 February 2015). We included randomized trials of oral supplements of all marine oils compared with a control in arthritis patients. The internal validity was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool and heterogeneity was explored using restricted maximum of likelihood (REML)-based meta-regression analysis. Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) was used to rate the overall quality of the evidence. Forty-two trials were included; 30 trials reported complete data on pain. The standardized mean difference (SMD) suggested a favorable effect (-0.24; 95% confidence interval, CI, -0.42 to -0.07; heterogeneity, I² = 63%. A significant effect was found in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (22 trials; -0.21; 95% CI, -0.42 to -0.004) and other or mixed diagnoses (3 trials; -0.63; 95% CI, -1.20 to -0.06), but not in osteoarthritis patients (5 trials; -0.17; 95% CI, -0.57-0.24). The evidence for using marine oil to alleviate pain in arthritis patients was overall of low quality, but of moderate quality in rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Keywords: arthritis; complementary medicine; fish oil; joint pain; marine oil; meta-analysis; randomized controlled trials; rheumatology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
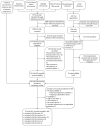
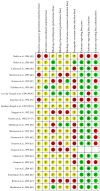
 : adequate methodology,
: adequate methodology,  : unclear methodology,
: unclear methodology,  : inadequate methodology. Risk of outcome reporting bias was not assessed for Vargová et al. (1998) [49], since only the abstract was available in English, and the rest of the article was not in English. Therefore, it was not considered appropriate to assess outcome reporting bias based only on the abstract of a full article.
: inadequate methodology. Risk of outcome reporting bias was not assessed for Vargová et al. (1998) [49], since only the abstract was available in English, and the rest of the article was not in English. Therefore, it was not considered appropriate to assess outcome reporting bias based only on the abstract of a full article.
 : adequate methodology,
: adequate methodology,  : unclear methodology,
: unclear methodology,  : inadequate methodology. Risk of outcome reporting bias was not assessed for Vargová et al. (1998) [49], since only the abstract was available in English, and the rest of the article was not in English. Therefore, it was not considered appropriate to assess outcome reporting bias based only on the abstract of a full article.
: inadequate methodology. Risk of outcome reporting bias was not assessed for Vargová et al. (1998) [49], since only the abstract was available in English, and the rest of the article was not in English. Therefore, it was not considered appropriate to assess outcome reporting bias based only on the abstract of a full article.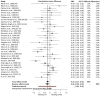
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

