FGF19/FGFR4 signaling contributes to the resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib
- PMID: 28069043
- PMCID: PMC5223586
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-016-0478-9
FGF19/FGFR4 signaling contributes to the resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib
Abstract
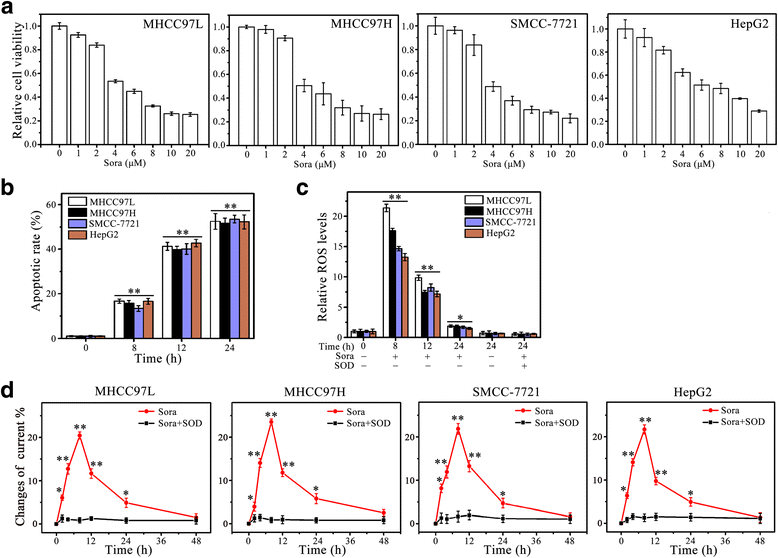
Background: Sorafenib, a multi-kinase inhibitor, is used as a standard therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, complete remission has not been achieved and the molecular basis of HCC resistance to sorafenib remains largely unknown. Previous studies have shown that fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19) expression correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis of HCC. Here, we demonstrate the novel role of FGF19 in HCC resistance to sorafenib therapy.
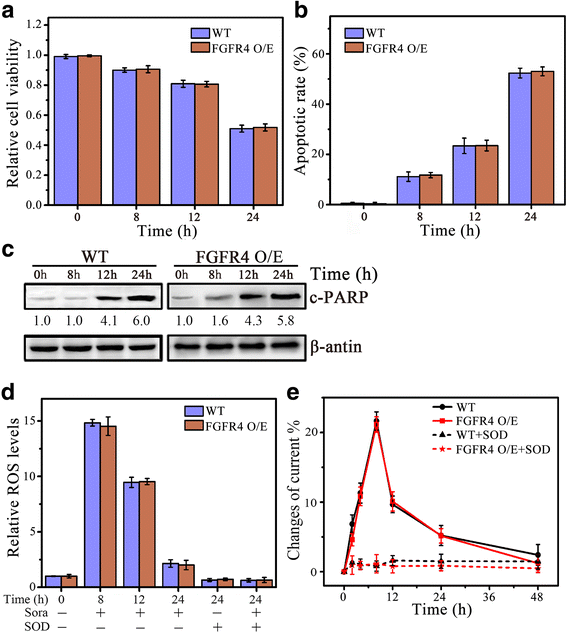
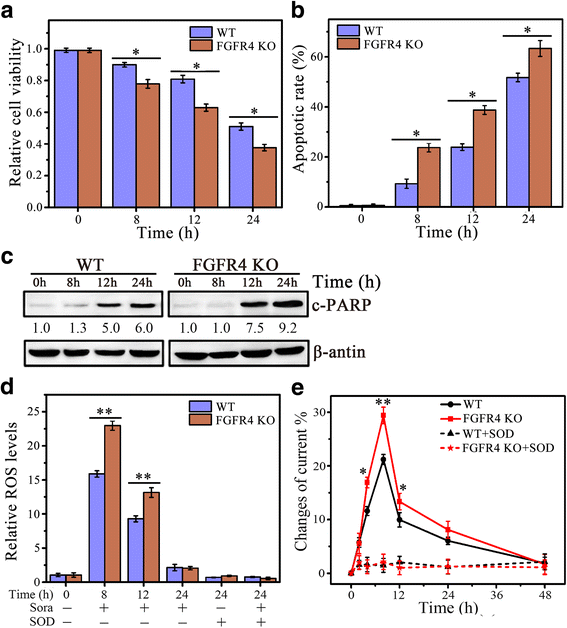
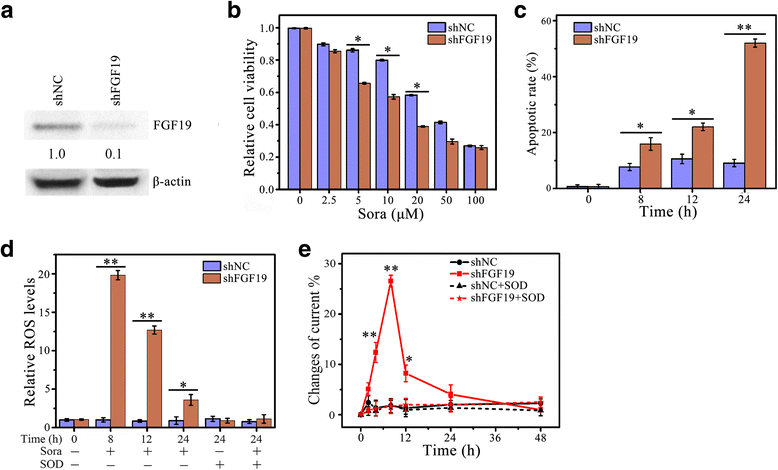
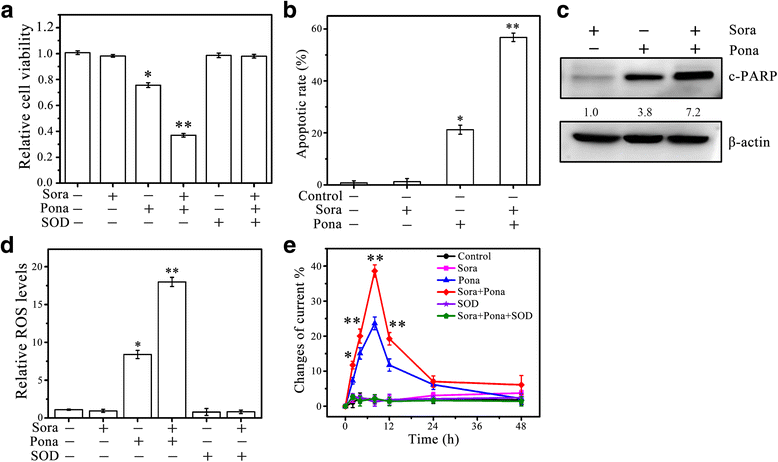
Methods: FGF19 Knockdown cells were achieved by lentiviral-mediated interference, and FGFR4 knockout cells were achieved by CRISPR-Cas9. Protein levels of FGF19, FGFR4 and c-PARP in various HCC cell lines were measured by Western blotting analysis. Cell viability was determined by MTS assay, apoptosis was determined by DAPI nuclear staining and Western blot of c-PRAP, and ROS generation was determined by DCFH-DA staining and electrochemical biosensor.
Results: We showed that FGF19, when overexpressed, inhibited the effect of sorafenib on ROS generation and apoptosis in HCC. In contrast, loss of FGF19 or its receptor FGFR4 led to a remarkable increase in sorafenib-induced ROS generation and apoptosis. In addition, knockdown of FGF19 in sorafenib-resistant HCC cells significantly enhanced the sensitivity to sorafenib. Importantly, targeting FGF19/FGFR4 axis by ponatinib, a third-generation inhibitor of chronic myeloid leukemia, overcomes HCC resistance of sorafenib by enhancing ROS-associated apoptosis in sorafenib-treated HCC.
Conclusion: Our results provide the first evidence that inhibition of FGF19/FGFR4 signaling significantly overcomes sorafenib resistance in HCC. Co-treatment of ponatinib and sorafinib may represent an effective therapeutic approach for eradicating HCC.
Keywords: Drug resistance; FGF19; FGFR4; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Sorafenib; Synergistic effect.
Figures

References
-
- Memon K, Kulik L, Lewandowski RJ, Mulcahy MF, Benson AB, Ganger D, et al. Radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis: impact of liver function on systemic treatment options at disease progression. J Hepatol. 2013;58:73–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.09.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang TS, Huang Y-H. Role of SENP1 in HBx-induced cell migration and stemness-related properties in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2016;76:1720–20. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2016-1720. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

