The ribosomal transcription units of Haplorchis pumilio and H. taichui and the use of 28S rDNA sequences for phylogenetic identification of common heterophyids in Vietnam
- PMID: 28069063
- PMCID: PMC5223338
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-017-1968-0
The ribosomal transcription units of Haplorchis pumilio and H. taichui and the use of 28S rDNA sequences for phylogenetic identification of common heterophyids in Vietnam
Abstract
Background: Heterophyidiasis is now a major public health threat in many tropical countries. Species in the trematode family Heterophyidae infecting humans include Centrocestus formosanus, Haplorchis pumilio, H. taichui, H. yokogawai, Procerovum varium and Stellantchasmus falcatus. For molecular phylogenetic and systematic studies on trematodes, we need more prospective markers for taxonomic identification and classification. This study provides near-complete ribosomal transcription units (rTU) from Haplorchis pumilio and H. taichui and demonstrates the use of 28S rDNA sequences for identification and phylogenetic analysis.
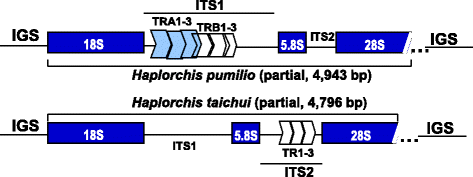
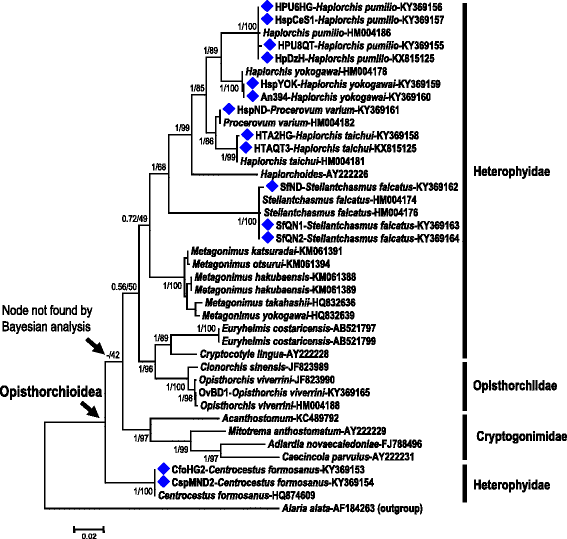
Results: The near-complete ribosomal transcription units (rTU), consisting of 18S, ITS1, 5.8S, ITS2 and 28S rRNA genes and spacers, from H. pumilio and H. taichui from human hosts in Vietnam, were determined and annotated. Sequence analysis revealed tandem repetitive elements in ITS1 in H. pumilio and in ITS2 in H. taichui. A phylogenetic tree inferred from 28S rDNA sequences of 40 trematode strains/species, including 14 Vietnamese heterophyid individuals, clearly confirmed the status of each of the Vietnamese species: Centrocestus formosanus, Haplorchis pumilio, H. taichui, H. yokogawai, Procerovum varium and Stellantchasmus falcatus. However, the family Heterophyidae was clearly not monophyletic, with some genera apparently allied with other families within the superfamily Opisthorchioidea (i.e. Cryptogonimidae and Opisthorchiidae). These families and their constituent genera require substantial re-evaluation using a combination of morphological and molecular data. Our new molecular data will assist in such studies.
Conclusions: The 28S rDNA sequences are conserved among individuals within a species but varied between genera. Based on analysis of 40 28S rDNA sequences representing 19 species in the superfamily Opisthorchioidea and an outgroup taxon (Alaria alata, family Diplostomidae), six common human pathogenic heterophyids were identified and clearly resolved. The phylogenetic tree inferred from these sequences again confirmed anomalies in molecular placement of some members of the family Heterophyidae and demonstrates the need for reappraisal of the entire superfamily Opisthorchioidea. The new sequences provided here supplement those already available in public databases and add to the array of molecular tools that can be used for the diagnosis of heterophyid species in human and animal infections.
Keywords: 28S rDNA sequence; Haplorchis pumilio; Haplorchis taichui; Heterophyidae; Phylogeny; Ribosomal transcription unit.
Figures
References
-
- Pearson J. Family Heterophyidae Leiper, 1909. In: Bray RA, Gibson DI, Jones A, editors. Keys to the Trematoda. London: CAB International and Natural History Museum UK; 2008. pp. 113–42.
-
- Cribb T, Gibson D. Heterophyidae Leiper, 1909. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species. 2010. http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=108441. Accessed 12 Oct 2016.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

