Cooperative Substrate-Cofactor Interactions and Membrane Localization of the Bacterial Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) Enzyme, ExoU
- PMID: 28069812
- PMCID: PMC5336173
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.760074
Cooperative Substrate-Cofactor Interactions and Membrane Localization of the Bacterial Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) Enzyme, ExoU
Abstract
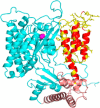
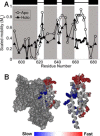
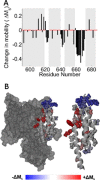
The ExoU type III secretion enzyme is a potent phospholipase A2 secreted by the Gram-negative opportunistic pathogen, Pseudomonas aeruginosa Activation of phospholipase activity is induced by protein-protein interactions with ubiquitin in the cytosol of a targeted eukaryotic cell, leading to destruction of host cell membranes. Previous work in our laboratory suggested that conformational changes within a C-terminal domain of the toxin might be involved in the activation mechanism. In this study, we use site-directed spin-labeling electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy to investigate conformational changes in a C-terminal four-helical bundle region of ExoU as it interacts with lipid substrates and ubiquitin, and to examine the localization of this domain with respect to the lipid bilayer. In the absence of ubiquitin or substrate liposomes, the overall structure of the C-terminal domain is in good agreement with crystallographic models derived from ExoU in complex with its chaperone, SpcU. Significant conformational changes are observed throughout the domain in the presence of ubiquitin and liposomes combined that are not observed with either liposomes or ubiquitin alone. In the presence of ubiquitin, two interhelical loops of the C-terminal four-helix bundle appear to penetrate the membrane bilayer, stabilizing ExoU-membrane association. Thus, ubiquitin and the substrate lipid bilayer act synergistically to induce a conformational rearrangement in the C-terminal domain of ExoU.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa); electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR); phospholipase; protein structure; ubiquitin.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

References
-
- Yahr T. L., Goranson J., and Frank D. W. (1996) Exoenzyme S of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is secreted by a type III pathway. Mol. Microbiol. 22, 991–1003 - PubMed
-
- Finck-Barbançon V., Goranson J., Zhu L., Sawa T., Wiener-Kronish J. P., Fleiszig S. M., Wu C., Mende-Mueller L., and Frank D. W. (1997) ExoU expression by Pseudomonas aeruginosa correlates with acute cytotoxicity and epithelial injury. Mol. Microbiol. 25, 547–557 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

