Purification of Zika virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and its use to identify small-molecule Zika inhibitors
- PMID: 28069884
- PMCID: PMC5890664
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkw514
Purification of Zika virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and its use to identify small-molecule Zika inhibitors
Abstract
Background: The viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) enzymes of the Flaviviridae family are essential for viral replication and are logically important targets for development of antiviral therapeutic agents. Zika virus (ZIKV) is a rapidly re-emerging human pathogen for which no vaccine or antiviral agent is currently available.
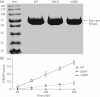
Methods: To facilitate development of ZIKV RdRp inhibitors, we have established an RdRp assay using purified recombinant ZIKV NS5 polymerase.
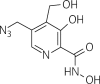
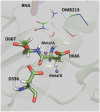
Results: We have shown that both the hepatitis C virus (HCV) nucleoside inhibitor sofosbuvir triphosphate and a pyridoxine-derived non-nucleoside small-molecule inhibitor, DMB213, can act against ZIKV RdRp activity at IC 50 s of 7.3 and 5.2 μM, respectively, in RNA synthesis reactions catalysed by recombinant ZIKV NS5 polymerase. Cell-based assays confirmed the anti-ZIKV activity of sofosbuvir and DMB213 with 50% effective concentrations (EC 50 s) of 8.3 and 4.6 μM, respectively. Control studies showed that DMB213 did not inhibit recombinant HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and showed only very weak inhibition of HIV-1 integrase strand-transfer activity. The S604T substitution in motif B of the ZIKV RdRp, which corresponds to the S282T substitution in motif B of HCV RdRp, which confers resistance to nucleotide inhibitors, also conferred resistance to sofosbuvir triphosphate, but not to DMB213. Enzyme assays showed that DMB213 appears to be competitive with natural nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) substrates.
Conclusions: Recombinant ZIKV RdRp assays can be useful tools for the screening of both nucleos(t)ide compounds and non-nucleotide metal ion-chelating agents that interfere with ZIKV replication.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery of a non-nucleoside RNA polymerase inhibitor for blocking Zika virus replication through in silico screening.Antiviral Res. 2018 Mar;151:78-86. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.12.016. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Antiviral Res. 2018. PMID: 29274845
-
Analysis of Ribonucleotide 5'-Triphosphate Analogs as Potential Inhibitors of Zika Virus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase by Using Nonradioactive Polymerase Assays.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Feb 23;61(3):e01967-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01967-16. Print 2017 Mar. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 27993851 Free PMC article.
-
Non-nucleoside Inhibitors of Zika Virus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase.J Virol. 2020 Oct 14;94(21):e00794-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00794-20. Print 2020 Oct 14. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32796069 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Potent Non-nucleoside Inhibitors of Dengue Viral RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase from Fragment Screening and Structure-Guided Design.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1062:187-198. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-8727-1_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29845534 Review.
-
The dengue virus NS5 protein as a target for drug discovery.Antiviral Res. 2015 Jul;119:57-67. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.04.010. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Antiviral Res. 2015. PMID: 25912817 Review.
Cited by
-
Antiviral effects of the fused tricyclic derivatives of indoline and imidazolidinone on ZIKV infection and RdRp activities of ZIKV and DENV.Virus Res. 2023 Mar;326:199062. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2023.199062. Epub 2023 Feb 7. Virus Res. 2023. PMID: 36746341 Free PMC article.
-
Sophoraflavenone G Restricts Dengue and Zika Virus Infection via RNA Polymerase Interference.Viruses. 2017 Oct 3;9(10):287. doi: 10.3390/v9100287. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28972551 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of Selected Nucleoside Analogue ProTides against Zika Virus in Human Neural Stem Cells.Viruses. 2019 Apr 20;11(4):365. doi: 10.3390/v11040365. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31010044 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the discovery of potent RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase (RdRp) inhibitors targeting viruses.RSC Med Chem. 2020 Dec 23;12(3):306-320. doi: 10.1039/d0md00318b. eCollection 2021 Mar 1. RSC Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 34046618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the RdRp of Emerging RNA Viruses: The Structure-Based Drug Design Challenge.Molecules. 2020 Dec 3;25(23):5695. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235695. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33287144 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Westaway EG, Brinton MA, Gaidamovich S. et al. Flaviviridae. Intervirology 1985; 24: 183–92. - PubMed
-
- Harris E, Holden KL, Edgil D. et al. Molecular biology of flaviviruses. Novartis Found Symp 2006; 277: 23–39. - PubMed
-
- Dick GW, Kitchen SF, Haddow AJ. Zika virus. I. Isolations and serological specificity. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1952; 46: 509–20. - PubMed
-
- Tognarelli J, Ulloa S, Villagra E. et al. A report on the outbreak of Zika virus on Easter Island, South Pacific, 2014. Arch Virol 2016; 161: 665–8. - PubMed
-
- Duffy MR, Chen TH, Hancock WT. et al. Zika virus outbreak on Yap Island, Federated States of Micronesia. N Engl J Med 2009; 360: 2536–43. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

