Interleukin 37 expression in mice alters sleep responses to inflammatory agents and influenza virus infection
- PMID: 28070566
- PMCID: PMC5218600
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbscr.2016.11.005
Interleukin 37 expression in mice alters sleep responses to inflammatory agents and influenza virus infection
Abstract
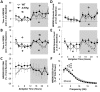
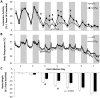
Multiple interactions between the immune system and sleep are known, including the effects of microbial challenge on sleep or the effects of sleep loss on facets of the immune response. Cytokines regulate, in part, sleep and immune responses. Here we examine the role of an anti-inflammatory cytokine, interleukin-37 (IL-37) on sleep in a mouse strain that expresses human IL-37b (IL37tg mice). Constitutive expression of the IL-37 gene in the brains of these mice under resting conditions is low; however, upon an inflammatory stimulus, expression increases dramatically. We measured sleep in three conditions; a) under baseline conditions and after 6 h of sleep loss, b) after bolus intraperitoneal administration of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or IL-1β and c) after intranasal influenza virus challenge. Under baseline conditions, the IL37tg mice had 7% more spontaneous non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREMS) during the light period than wild-type (WT) mice. After sleep deprivation both WT mice and IL37tg mice slept an extra 21% and 12%, respectively, during the first 6 h of recovery. NREMS responses after sleep deprivation did not significantly differ between WT mice and IL37tg mice. However, in response to either IL-1β or LPS, the increases in time spent in NREMS were about four-fold greater in the WT mice than in the IL37tg mice. In contrast, in response to a low dose of mouse-adapted H1N1 influenza virus, sleep responses developed slowly over the 6 day recording period. By day 6, NREMS increased by 10% and REMS increased by 18% in the IL37tg mice compared to the WT mice. Further, by day 4 IL37tg mice lost less weight, remained more active, and retained their body temperatures closer to baseline values than WT mice. We conclude that conditions that promote IL-37 expression attenuate morbidity to severe inflammatory challenge.
Keywords: IL-1F7; IL-37; body weight; influenza virus H1N1; interleukin-1β; lipopolysaccharide; sleep deprivation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Diurnal variation of lipopolysaccharide-induced alterations in sleep and body temperature of interleukin-6-deficient mice.Brain Behav Immun. 2005 Jan;19(1):40-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2004.04.001. Brain Behav Immun. 2005. PMID: 15581737
-
The neuron-specific interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein is required for homeostatic sleep and sleep responses to influenza viral challenge in mice.Brain Behav Immun. 2015 Jul;47:35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.10.013. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Brain Behav Immun. 2015. PMID: 25449578 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep-wake behavior and responses of interleukin-6-deficient mice to sleep deprivation.Brain Behav Immun. 2005 Jan;19(1):28-39. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2004.02.003. Brain Behav Immun. 2005. PMID: 15581736
-
Counterpointing the functional role of the forebrain and of the brainstem in the control of the sleep-waking system.J Sleep Res. 2004 Sep;13(3):179-208. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2869.2004.00412.x. J Sleep Res. 2004. PMID: 15339255 Review.
-
Microbial Products and Cytokines in Sleep and Fever Regulation.Crit Rev Immunol. 2017;37(2-6):291-315. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.v37.i2-6.70. Crit Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29773024 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenetical and Neurophysiological Features of Patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Phenomena and Diagnoses.J Clin Med. 2019 Oct 2;8(10):1588. doi: 10.3390/jcm8101588. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31581672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effect of IL-37-Producing T-Cell Population in DSS-Induced Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 5;19(12):3884. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123884. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30563054 Free PMC article.
-
Performance on the mouse vibration actuating search task is compromised by sleep deprivation.J Neurophysiol. 2020 Feb 1;123(2):600-607. doi: 10.1152/jn.00826.2018. Epub 2019 Dec 31. J Neurophysiol. 2020. PMID: 31891527 Free PMC article.
-
The Associations of Serum IL-37 With the Severity and Prognosis in Patients With Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Front Immunol. 2021 May 7;12:636896. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636896. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34025645 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-37 suppresses the osteogenic responses of human aortic valve interstitial cells in vitro and alleviates valve lesions in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Feb 14;114(7):1631-1636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1619667114. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28137840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alt J.A., Bohnet S., Taishi P., Duricka D., Obal F., Jr, Traynor T., Majde J.A., Krueger J.M. Influenza virus-induced glucocorticoid and hypothalamic and lung cytokine mRNA responses in dwarf lit/lit mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2007;21:60–67. - PubMed
-
- Bettis R., Iacuzio D., Jung T., Fuchs R., Aultman R., Gyldmark M. Impact of influenza treatment with oseltamivir on health, sleep and daily activities of otherwise healthy adults and adolescents. Clin. Drug Investig. 2006;26:329–340. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
