Photo-reduced Cu/CuO nanoclusters on TiO2 nanotube arrays as highly efficient and reusable catalyst
- PMID: 28071708
- PMCID: PMC5223138
- DOI: 10.1038/srep39695
Photo-reduced Cu/CuO nanoclusters on TiO2 nanotube arrays as highly efficient and reusable catalyst
Abstract
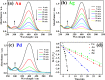
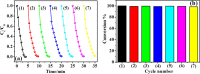
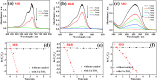
Non-noble metal nanoparticles are becoming more and more important in catalysis recently. Cu/CuO nanoclusters on highly ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays are successfully developed by a surfactant-free photoreduction method. This non-noble metal Cu/CuO-TiO2 catalyst exhibits excellent catalytic activity and stability for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) to 4-aminophenol (4-AP) with the presence of sodium borohydride (NaBH4). The rate constant of this low-cost Cu/CuO based catalyst is even higher than that of the noble metal nanoparticles decorated on the same TiO2 substrate. The conversion efficiency remains almost unchanged after 7 cycles of recycling. The recycle process of this Cu/CuO-TiO2 catalyst supported by Ti foil is very simple and convenient compared with that of the common powder catalysts. This catalyst also exhibited great catalytic activity to other organic dyes, such as methylene blue (MB), rhodamine B (RhB) and methyl orange (MO). This highly efficient, low-cost and easily reusable Cu/CuO-TiO2 catalyst is expected to be of great potential in catalysis in the future.
Figures

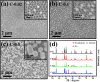
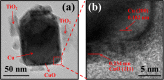
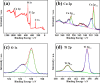
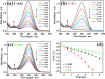
References
-
- Narayanan K. B. & Sakthivel N. Heterogeneous catalytic reduction of anthropogenic pollutant, 4-nitrophenol by silver-bionanocomposite using Cylindrocladium floridanum. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 10737–10740 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Pocurull E., Marcé R. M. & Borrull F. Determination of phenolic compounds in natural waters by liquid chromatography with ultraviolet and electrochemical detection after on-line trace enrichment. J. Chromatogr. A 738, 1–9 (1996).
-
- Feng J. et al. CuFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles: A simple and efficient catalyst for the reduction of nitrophenol. Chem. Eng. J. 221, 16–24 (2013).
-
- Li J. et al. A graphene oxide-based electrochemical sensor for sensitive determination of 4-nitrophenol. J. Hazard. Mater. 201–202, 250–259 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Zhang S. H. et al. In situ assembly of well-dispersed Ni nanoparticles on silica nanotubes and excellent catalytic activity in 4-nitrophenol reduction. Nanoscale 6, 11181–11188 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

