Comparison of jet injector and insulin pen in controlling plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in type 2 diabetic patients
- PMID: 28072690
- PMCID: PMC5228650
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005482
Comparison of jet injector and insulin pen in controlling plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in type 2 diabetic patients
Abstract
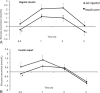
This study is conducted to investigate efficacy of an insulin jet injector and an insulin pen in treatment of type 2 diabetic patients. Sixty patients with type 2 diabetes were treated with rapid-acting insulin (regular insulin) and insulin analog (insulin aspart) using the jet injector and the pen in 4 successive test cycles. Postprandial glucose and insulin concentrations in blood were measured over time. Areas under curves of glucose and the insulin were calculated, and efficacy of 2 injection methods in treatment of the diabetes was compared. Regular insulin and insulin aspart administration by the jet injector showed significant decreases in plasma glucose levels as compared to the pen injection (P < 0.05). Postprandial plasma glucose excursions at the time points of 0.5 to 3 hours were obviously lower in the jet-treated patients than the pen-treated ones (P < 0.05). Postprandial plasma insulin levels were markedly higher in the jet-treated patients than the pen-treated ones (P < 0.05). Area under the glucose curve in the pen-treated patients was significantly increased as compared to the jet-treated ones (P < 0.01). Efficacy of the insulin jet injector in treatment of type 2 diabetic patients is obviously superior to the insulin pen in regulating plasma glucose and insulin levels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Sonoki K, Yoshinari M, Iwase M, et al. Regurgitation of blood into insulin cartridges in the pen-like injectors. Diabetes Care 2001;24:603–4. - PubMed
-
- Baxter J, Mitragotri S. Jet-induced skin puncture and its impact on needle-free jet injections: experimental studies and a predictive model. J Control Release 2005;106:361–73. - PubMed
-
- Park CH, Tijing LD, Kim CS, et al. Needle-free transdermal delivery using PLGA nanoparticles: effect of particle size, injection pressure and syringe orifice diameter. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2014;123:710–5. - PubMed
-
- Schramm-Baxter J, Mitragotri S. Needle-free jet injections: dependence of jet penetration and dispersion in the skin on jet power. J Control Release 2004;97:527–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

