Effect of hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy (HITHOC) on the malignant pleural effusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 28072694
- PMCID: PMC5228654
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005532
Effect of hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy (HITHOC) on the malignant pleural effusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Although hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) has been widely used to treat malignant ascites or as a preventive strategy for microscopic carcinomatosis following surgical resection of abdominal tumors, application of hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy (HITHOC) in the treatment of malignant pleural effusion is limited. The objective of the current study was to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis on the application of HITHOC in the palliative treatment of malignant pleural effusion.
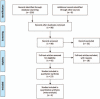
Methods: After thorough searching of online databases, total 27 articles were included into qualitative systematic review and 5 of them were used to conduct qualitative meta-analysis.
Results: It was found that most of HITHOC was used in combination of cytoreductive surgery (CRS) including pleurectomy/decortication or after surgical resection of primary tumors, which mainly were lung cancer, thymoma or thymic carcinoma, breast cancer, and ovarian cancer. Patients who received HITHOC had significantly longer median survival length compared to the patients without HITHOC (Hedges g = 0.763, P < 0.001). In addition, HITHOC therapy was favored (Hedges g = 0.848, P < 0.001) in terms of median survival length, tumor-free survival rate, with tumor survival rate or Karnofsky performance status (KPS) scale.
Conclusion: HITHOC is a safe and effective therapy in controlling pleural effusion and increasing patient's survival rate.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma after cytoreductive surgical procedures: a systematic review.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 Apr 9;23(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03748-8. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40205604 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intrathoracic Chemotherapy (HITHOC) in Thymic Neoplasia: A Systematic Review and Single-Arm Meta-analysis.Ann Surg Oncol. 2025 Mar;32(3):1670-1678. doi: 10.1245/s10434-024-16547-4. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Ann Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39604748
-
Hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy (HITHOC) in stage IVA thymomas: a narrative review.Mediastinum. 2025 Jun 25;9:16. doi: 10.21037/med-25-8. eCollection 2025. Mediastinum. 2025. PMID: 40666533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytoreductive surgery with hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma: a systematic review.Thorax. 2023 Apr;78(4):409-417. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2021-218214. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Thorax. 2023. PMID: 35410957
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
Cited by
-
The Evolving Role of Chemotherapy in the Management of Pleural Malignancies: Current Evidence and Future Directions.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 25;17(13):2143. doi: 10.3390/cancers17132143. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outcome after cytoreductive surgery combined with hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy in patients with secondary pleural metastases.Front Oncol. 2023 Nov 28;13:1259779. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1259779. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38090507 Free PMC article.
-
Abrupt hemodynamic changes accompanying intrapleural hyperthermic chemotherapy: Case series.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jun;97(25):e10982. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010982. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29923981 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal Treatment Including Intracavitary Chemotherapy for Recurrent Pediatric Pleuropulmonary Blastoma.Cureus. 2021 Dec 21;13(12):e20584. doi: 10.7759/cureus.20584. eCollection 2021 Dec. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 35103161 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy (HITHOC) should be included in the guidelines for malignant pleural mesothelioma.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Jun;9(11):960. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-7247. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34350275 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- American Thoracic Society Management of malignant pleural effusions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;162:1987–2001. - PubMed
-
- Erasmus JJ, Goodman PC, Patz EF., Jr Management of malignant pleural effusions and pneumothorax. Radiol Clin North Am 2000;38:375–83. - PubMed
-
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 2002;21:1539–58. - PubMed
-
- Matsuzaki Y, Shibata K, Yoshioka M, et al. Intrapleural perfusion hyperthermo-chemotherapy for malignant pleural dissemination and effusion. Ann Thorac Surg 1995;59:127–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

