Two new karlotoxins found in Karlodinium veneficum (strain GM2) from the East China Sea
- PMID: 28073460
- PMCID: PMC5228562
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hal.2016.08.001
Two new karlotoxins found in Karlodinium veneficum (strain GM2) from the East China Sea
Abstract
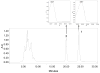
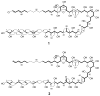
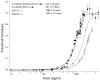
The dinoflagellate Karlodinium veneficum is a harmful algal bloom species with a worldwide distribution. This small athecate dinoflagellate makes a family of polyketide toxins that are hemolytic, cytotoxic and ichthyotoxic. The first chemical structure for karlotoxins from East China Sea (ECS) is reported here. The two new karlotoxins, namely 4,5-dihydro-KmTx 2 (compound 1) and 4,5-dihydro-dechloro-KmTx 2 (compound 2), were isolated and purified from monoalgal cultures of K. veneficum strain GM2. Their structures were determined by spectroscopic analysis, including tandem mass spectrometry as well as 1D and 2D NMR experiments. These new karlotoxin congeners feature a saturated polyol arm different from previously reported for KmTx 2 that appears to increase hemolytic activity.
Keywords: Dinoflagellate; East China Sea; Hemolysis; Karlodinium veneficum; Karlotoxin.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
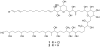

Similar articles
-
LC-MS/MS Detection of Karlotoxins Reveals New Variants in Strains of the Marine Dinoflagellate Karlodinium veneficum from the Ebro Delta (NW Mediterranean).Mar Drugs. 2017 Dec 18;15(12):391. doi: 10.3390/md15120391. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 29258236 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and relative potency of several karlotoxins from Karlodinium veneficum.J Nat Prod. 2010 Aug 27;73(8):1360-5. doi: 10.1021/np100158r. J Nat Prod. 2010. PMID: 20795740 Free PMC article.
-
A preliminary study on the allelopathy and toxicity of the dinoflagellate Karlodinium veneficum.Mar Pollut Bull. 2020 Sep;158:111400. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111400. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Mar Pollut Bull. 2020. PMID: 32753185
-
Emerging harmful algal bloom species over the last four decades in China.Harmful Algae. 2022 Jan;111:102059. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2021.102059. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Harmful Algae. 2022. PMID: 35016757 Review.
-
The expanding role of marine microbes in pharmaceutical development.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2010 Dec;21(6):780-6. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2010.09.013. Epub 2010 Oct 16. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20956080 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of benthol A and its challenging stereochemical assignment: opening up a new window for skeletal diversity of super-carbon-chain compounds.Chem Sci. 2021 Jun 30;12(30):10197-10206. doi: 10.1039/d1sc02810c. eCollection 2021 Aug 4. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34447528 Free PMC article.
-
The blue mussel Mytilus edulis is vulnerable to the toxic dinoflagellate Karlodinium armiger-Adult filtration is inhibited and several life stages killed.PLoS One. 2018 Jun 18;13(6):e0199306. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199306. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29912948 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally Occurring Organohalogen Compounds-A Comprehensive Review.Prog Chem Org Nat Prod. 2023;121:1-546. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-26629-4_1. Prog Chem Org Nat Prod. 2023. PMID: 37488466 Review.
-
Nanopore Sequencing of Amoebophrya Species Reveals Novel Collection of Bacteria Putatively Associated With Karlodinium veneficum.Genome Biol Evol. 2025 Mar 6;17(3):evaf022. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evaf022. Genome Biol Evol. 2025. PMID: 39943733 Free PMC article.
-
Karmitoxin: An Amine-Containing Polyhydroxy-Polyene Toxin from the Marine Dinoflagellate Karlodinium armiger.J Nat Prod. 2017 May 26;80(5):1287-1293. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00860. Epub 2017 Apr 5. J Nat Prod. 2017. PMID: 28379705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adolf JE, Bachvaroff T, Place AR. Can cryptophyte abundance trigger toxic Karlodinium veneficum blooms in eutrophic estuaries? Harmful Algae. 2008;8:119–128.
-
- Adolf JE, Krupatkina D, Bachvaroff T, Place AR. Karlotoxin mediates grazing by Oxyrrhis marina on strains of Karlodinium veneficum. Harmful Algae. 2007;6:400–412.
-
- Adolf JE, Bachvaroff T, Krupatkina DN, Nonogaki H, Brown PJP, Lewitus AJ. Species specificity and potential roles of Karlodinium micrum toxin. Afr J Mar Sci. 2006a;28:415–421.
-
- Adolf JE, Stoecker DK, Harding LW. The balance of autotrophy and heterotrophy during mixotrophic growth of Karlodinium micrum (Dinophyceae) J Plankton Res. 2006b;28:737–751.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

