Massive donor transfusion potentially increases recipient mortality after lung transplantation
- PMID: 28073574
- PMCID: PMC5392422
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2016.12.006
Massive donor transfusion potentially increases recipient mortality after lung transplantation
Abstract
Objective: Donor blood transfusion has been identified as a potential risk factor for primary graft dysfunction and by extension early mortality. We sought to define the contributing risk of donor transfusion on early mortality for lung transplant.
Methods: Donor and recipient data were abstracted from the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network database updated through June 30, 2014, which included 86,398 potential donors and 16,255 transplants. Using the United Network for Organ Sharing 4-level designation of transfusion (no blood, 1-5 units, 6-10 units, and >10 units, massive), we analyzed all-cause mortality at 30-days with the use of logistic regression adjusted for confounders (ischemic time, donor age, recipient diagnosis, lung allocation score and recipient age, and recipient body mass index). Secondary analyses assessed 90-day and 1-year mortality and hospital length of stay.
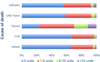
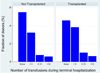
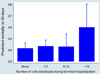
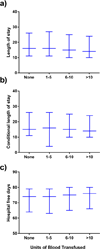
Results: Of the 16,255 recipients transplanted, 8835 (54.35%) donors received at least one transfusion. Among those transfused, 1016 (6.25%) received a massive transfusion, defined as >10 units. Those donors with massive transfusion were most commonly young trauma patients. After adjustment for confounding variables, donor massive transfusion was associated significantly with an increased risk in 30-day (P = .03) and 90-day recipient mortality (P = .01) but not 1-year mortality (P = .09). There was no significant difference in recipient length of stay or hospital-free days with respect to donor transfusion.
Conclusions: Massive donor blood transfusion (>10 units) was associated with early recipient mortality after lung transplantation. Conversely, submassive donor transfusion was not associated with increased recipient mortality. The mechanism of increased early mortality in recipients of lungs from massively transfused donors is unclear and needs further study but is consistent with excess mortality seen with primary graft dysfunction in the first 90 days posttransplant.
Keywords: blood transfusion; lung transplantation.
Copyright © 2016 The American Association for Thoracic Surgery. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors affirm no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
TRALI by proxy.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017 May;153(5):1204-1205. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2017.01.036. Epub 2017 Feb 7. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017. PMID: 28314528 No abstract available.
References
-
- Naik PM, Angel LF. Special issues in the management and selection of the donor for lung transplantation. Seminars in immunopathology. 2011;33(2):201–210. - PubMed
-
- Christie JD, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: 29th adult lung and heart-lung transplant report-2012. The Journal of heart and lung transplantation : the official publication of the International Society for Heart Transplantation. 2012;31(10):1073–1086. - PubMed
-
- Valapour M, Paulson K, Smith JM, et al. OPTN/SRTR 2011 Annual Data Report: lung. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons. 2013;13(Suppl 1):149–177. - PubMed
-
- Webert KE, Blajchman MA. Transfusion-related acute lung injury. Transfusion medicine reviews. 2003;17(4):252–262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

