Evidence that oxidative dephosphorylation by the nonheme Fe(II), α-ketoglutarate:UMP oxygenase occurs by stereospecific hydroxylation
- PMID: 28074470
- PMCID: PMC5380139
- DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.12554
Evidence that oxidative dephosphorylation by the nonheme Fe(II), α-ketoglutarate:UMP oxygenase occurs by stereospecific hydroxylation
Abstract
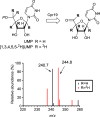
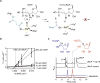
LipL and Cpr19 are nonheme, mononuclear Fe(II)-dependent, α-ketoglutarate (αKG):UMP oxygenases that catalyze the formation of CO2 , succinate, phosphate, and uridine-5'-aldehyde, the last of which is a biosynthetic precursor for several nucleoside antibiotics that inhibit bacterial translocase I (MraY). To better understand the chemistry underlying this unusual oxidative dephosphorylation and establish a mechanistic framework for LipL and Cpr19, we report herein the synthesis of two biochemical probes-[1',3',4',5',5'-2 H]UMP and the phosphonate derivative of UMP-and their activity with both enzymes. The results are consistent with a reaction coordinate that proceeds through the loss of one 2 H atom of [1',3',4',5',5'-2 H]UMP and stereospecific hydroxylation geminal to the phosphoester to form a cryptic intermediate, (5'R)-5'-hydroxy-UMP. Thus, these enzyme catalysts can additionally be assigned as UMP hydroxylase-phospholyases.
Keywords: antibiotic; biosynthesis; nonheme iron; nucleoside; oxygenase; translocase I.
© 2017 Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Figures
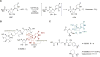


References
-
- Hausinger RP. Fe(II)/α-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases and related enzymes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2004;39:21–68. - PubMed
-
- Wu LF, Meng S, Tang GL. Ferrous iron and α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases in the biosynthesis of microbial natural products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1864:453–470. - PubMed
-
- Schofield C, Hausinger R. RSC Metatallobiology: 2-Oxoglutarate-Dependent Oxygenases. Royal Society of Chemistry; 2015.
-
- Bollinger JM, Krebs C. Stalking intermediates in oxygen activation by iron enzymes: Motivation and method. J Inorg Biochem. 2006;100:586–605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

