Comparison of respiratory motion suppression techniques for 4D flow MRI
- PMID: 28074541
- PMCID: PMC6084364
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.26574
Comparison of respiratory motion suppression techniques for 4D flow MRI
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this work was to assess the impact of respiratory motion and to compare methods for suppression of respiratory motion artifacts in 4D Flow MRI.
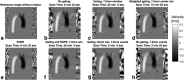
Methods: A numerical 3D aorta phantom was designed based on an aorta velocity field obtained by computational fluid mechanics. Motion-distorted 4D Flow MRI measurements were simulated and several different motion-suppression techniques were evaluated: Gating with fixed acceptance window size, gating with different window sizes in inner and outer k-space, and k-space reordering. Additionally, different spatial resolutions were simulated.
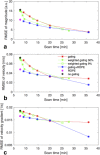
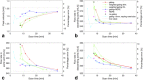
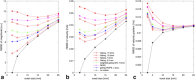
Results: Respiratory motion reduced the image quality. All motion-suppression techniques improved the data quality. Flow rate errors of up to 30% without gating could be reduced to less than 2.5% with the most successful motion suppression methods. Weighted gating and gating combined with k-space reordering were advantageous compared with conventional fixed-window gating. Spatial resolutions finer than the amount of accepted motion did not lead to improved results.
Conclusion: Respiratory motion affects 4D Flow MRI data. Several different motion suppression techniques exist that are capable of reducing the errors associated with respiratory motion. Spatial resolutions finer than the degree of accepted respiratory motion do not result in improved data quality. Magn Reson Med 78:1877-1882, 2017. © 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Keywords: 4D flow MRI; MR flow imaging; artifacts; image quality; motion suppression; navigator gating.
© 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Bailes D, Gilderdale D, Bydder G, Collins A, Firmin D. Respiratory ordered phase encoding (ROPE): a method for reducing respiratory motion artefacts in MR imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1985;9:835–838. - PubMed
-
- Xiang QS, Henkelman RM. K‐space description for MR imaging of dynamic objects. Magn Reson Med 1993;29:422–428. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Riederer SJ, Ehman RL. Respiratory motion of the heart: kinematics and the implications for the spatial resolution in coronary imaging. Magn Reson Med 1995;33:713–719. - PubMed
-
- Ehman RL, Felmlee JP. Adaptive technique for high‐definition MR imaging of moving structures. Radiology 1989;173:255–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

