EID3 directly associates with DNMT3A during transdifferentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to NPC-like cells
- PMID: 28074931
- PMCID: PMC5225425
- DOI: 10.1038/srep40463
EID3 directly associates with DNMT3A during transdifferentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to NPC-like cells
Abstract
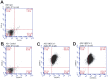
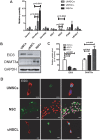
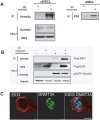
There has been recently been increased interest in the plasticity of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UMSCs) and their potential in the treatment of neurological disorders. In this study, UMSCs were transdifferentiated into neural stem-like cells (uNSCL), these cells grow in neurosphere-like structures and express high levels of NSCs markers. Epigenetics-related gene screening was here used to assess the relationship between E1A-like inhibitor of differentiation 3 (EID3), a p300 inhibitor, and DNA methyltransferase 3 A (DNMT3A) during the transdifferentiation of UMSCs into uNSCL in vitro. Before transdifferentiation of UMSCs into uNSCLs, high levels of EID3 and low levels of DNMT3A were detected; after transdifferentiation, low levels of EID3 and high levels of DNMT3A were detected. The current work showed that EID3 and DNMT3A co-localized in cell nuclei and EID3 interacted directly with DNMT3A in uNSCL. In summary, these results suggest that DNMT3A is probably directly regulated by EID3 during UMSC transdifferentiation into uNSCLs. These findings indicated a novel mechanism by which EID3, a p300 acetyltransferase inhibitor, could directly affect DNMT3A, this enzyme possesses dual methylation and demethylation abilities. These studies may be helpful for understanding a complex regulation mode of DNMT3A, which is a unique member of the methyltransferase family.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

