Poly(C)-binding protein 1 mediates drug resistance in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 28076324
- PMCID: PMC5355098
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14516
Poly(C)-binding protein 1 mediates drug resistance in colorectal cancer
Abstract
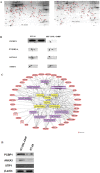
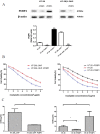
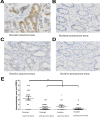
Oxaliplatin (L-OHP) is standard treatment for colorectal cancer. However, resistance to L-OHP often leads to treatment failure or cancer relapse. Understanding of the mechanism underlying L-OHP resistance is important to overcome the resistance and improve colorectal cancer treatment. This study aimed to identify new proteins that mediates L-OHP resistance in colorectal cancer and elucidate their mode of function. HT-29 cells were exposed to gradually increased concentration of L-OHP to select L-OHP resistant HT-29/L-OHP cell line. Proteomic analysis of HT-29 and HT-29/L-OHP cells were performed to identify differentially expressed proteins, including Poly(C)-binding protein 1 (PCBP1). PCBP1 expression level in 20 cases of L-OHP sensitive patients and 20 cases of L-OHP refractory patients was analyzed by immunohistochemistry. Chemoresistance and Akt activation in HT-29 and HT-29/L-OHP cells were analyzed by MTT assay and Western blot analysis. We identified 37 proteins showing differential expression in HT-29/L-OHP and HT-29 cells. In particular, PCBP1 protein level increased 15.6 fold in HT-29/L-OHP cells compared to HT-29 cells. Knockdown of PCBP1 sensitized HT-29/L-OHP and HT-29 cells to L-OHP, while overexpression of PCBP1 increased L-OHP resistance in HT-29 cells. In addition, PCBP1 expression was significantly higher in tumor samples from L-OHP refractory patients than in those from L-OHP responsive patients. Furthermore, we found that knockdown of PCBP1 inhibited the activation of Akt in HT-29/L-OHP and HT-29 cells. In conclusion, our findings suggest that PCBP1 is a molecular marker of L-OHP resistance in colorectal cancer and a promising target for colorectal cancer therapy.
Keywords: chemoresistance; colorectal cancer; oxaliplatin; poly(C)-binding protein 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Knudsen AB, Zauber AG, Rutter CM, Naber SK, Doria-Rose VP, Pabiniak C, Johanson C, Fischer SE, Lansdorp-Vogelaar I, Kuntz KM. Estimation of Benefits, Burden, and Harms of Colorectal Cancer Screening Strategies: Modeling Study for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;315:2595–2609. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sato S, Itamochi H, Kigawa J, Oishi T, Shimada M, Sato S, Naniwa J, Uegaki K, Nonaka M, Terakawa N. Combination chemotherapy of oxaliplatin and 5-fluorouracil may be an effective regimen for mucinous adenocarcinoma of the ovary: A potential treatment strategy. Cancer Sci. 2009;100:546–551. - PMC - PubMed
-
- El-akawi Z, Abu-hadid M, Perez R, Glavy J, Zdanowicz J, Creaven PJ, Pendyala L. Altered glutathione metabolism in oxaliplatin resistant ovarian carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 1996;105:5–14. - PubMed
-
- Arnould S, Hennebelle I, Canal P, Bugat R, Guichard S. Cellular determinants of oxaliplatin sensitivity in colon cancer cell lines. Eur J Cancer. 2003;39:112–119. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

