Body Dysmorphic Symptoms Scale for patients seeking esthetic surgery: cross-cultural validation study
- PMID: 28076636
- PMCID: PMC11448731
- DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2016.0068160416
Body Dysmorphic Symptoms Scale for patients seeking esthetic surgery: cross-cultural validation study
Abstract
Context and objective:: Rhinoplasty is one of the most sought-after esthetic operations among individuals with body dysmorphic disorder. The aim of this study was to cross-culturally adapt and validate the Body Dysmorphic Symptoms Scale.
Design and setting:: Cross-cultural validation study conducted in a plastic surgery outpatient clinic of a public university hospital.
Methods:: Between February 2014 and March 2015, 80 consecutive patients of both sexes seeking rhinoplasty were selected. Thirty of them participated in the phase of cultural adaptation of the instrument. Reproducibility was tested on 20 patients and construct validity was assessed on 50 patients, with correlation against the Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale for Body Dysmorphic Disorder.
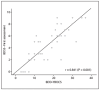
Results:: The Brazilian version of the instrument showed Cronbach's alpha of 0.805 and excellent inter-rater reproducibility (intraclass correlation coefficient, ICC = 0.873; P < 0.001) and intra-rater reproducibility (ICC = 0.939; P < 0.001). Significant differences in total scores were found between patients with and without symptoms (P < 0.001). A strong correlation (r = 0.841; P < 0.001) was observed between the Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale for Body Dysmorphic Disorder and the Body Dysmorphic Symptoms Scale. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.981, thus showing good accuracy for discriminating between presence and absence of symptoms of body dysmorphic disorder. Forty-six percent of the patients had body dysmorphic symptoms and 54% had moderate to severe appearance-related obsessive-compulsive symptoms.
Conclusions:: The Brazilian version of the Body Dysmorphic Symptoms Scale is a reproducible instrument that presents face, content and construct validity.
CONTEXTO E OBJETIVO:: Rinoplastia é uma das operações mais procuradas por indivíduos com o transtorno dismórfico corporal. O objetivo deste estudo foi adaptar culturalmente e validar a Body Dysmorphic Symptoms Scale.
DESENHO E LOCAL:: Estudo de validação cultural desenvolvido no ambulatório de cirurgia plástica de um hospital universitário público.
MÉTODOS:: Oitenta pacientes consecutivos de ambos os gêneros que desejavam submeter-se à rinoplastia foram selecionados entre fevereiro de 2014 e março de 2015. Trinta pacientes participaram da fase de adaptação cultural do instrumento. A reprodutibilidade foi testada em 20 pacientes e a validade de construto em 50 pacientes, correlacionando-se a escala com a Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale para transtorno dismórfico corporal.
RESULTADOS:: A versão brasileira do instrumento mostrou alfa de Cronbach de 0,805 e excelente reprodutibilidade interobservador (coeficiente de correlação intraclasse, CCI = 0,873; P < 0,001) e intraobservador (CCI = 0,939; P < 0,001). Houve diferença significante entre os escores totais de pacientes com e sem sintomas (P < 0,001). Observou-se forte correlação (r = 0,841; P < 0,001) entre a Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale para transtorno dismórfico corporal e a Body Dysmorphic Symptoms Scale. A área sob a curva característica de operação do receptor (ROC) foi de 0,981, revelando boa acurácia para discriminar a presença de sintomas para transtorno dismórfico corporal; 46% dos pacientes apresentaram sintomas do transtorno dismórfico corporal e 54% dos pacientes apresentaram sintomas obsessivo-compulsivos moderados a graves relacionados com a aparência.
CONCLUSÃO:: A versão brasileira da Body Dysmorphic Symptoms Scale é um instrumento reprodutível que apresenta validade de face, conteúdo e construto.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons . 2013 Plastic surgery statistics report. ASPS National Clearinghouse of Plastic Surgery Procedural Statistics. 2013. http://www.plasticsurgery.org/Documents/news-resources/statistics/2013-s... Accessed in 2016 (Apr 28)
-
- International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery . ISAPS International survey on aesthetic/cosmetic. Procedures performed in 2013. http://www.isaps.org/Media/Default/global-statistics/2014%20ISAPS%20Resu... Accessed in 2016 (Apr 28)
-
- Felix GA, de Brito MJ, Nahas FX, et al. Patients with mild to moderate body dysmorphic disorder may benefit from rhinoplasty. J Plast Reconstr Aesth Surg. 2014;67(5):646–654. - PubMed
-
- de Brito MJ, Nahas FX, Cordás TA, Tavares H, Ferreira LM. Body Dysmorphic Disorder in Patients Seeking Abdominoplasty, Rhinoplasty, and Rhytidectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;137(2):462–471. - PubMed
-
- Javo IM, Sørlie T. Psychosocial characteristics of young Norwegian women interested in liposuction, breast augmentation, rhinoplasty, and abdominoplasty: a population-based study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;125(5):1536–1543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

