Is CD47 an innate immune checkpoint for tumor evasion?
- PMID: 28077173
- PMCID: PMC5225552
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-016-0381-z
Is CD47 an innate immune checkpoint for tumor evasion?
Abstract
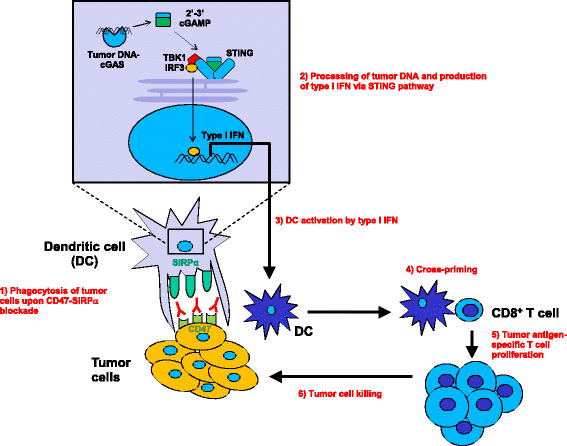
Cluster of differentiation 47 (CD47) (also known as integrin-associated protein) is a ubiquitously expressed glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin superfamily that plays a critical role in self-recognition. Various solid and hematologic cancers exploit CD47 expression in order to evade immunological eradication, and its overexpression is clinically correlated with poor prognoses. One essential mechanism behind CD47-mediated immune evasion is that it can interact with signal regulatory protein-alpha (SIRPα) expressed on myeloid cells, causing phosphorylation of the SIRPα cytoplasmic immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs and recruitment of Src homology 2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatases to ultimately result in delivering an anti-phagocytic-"don't eat me"-signal. Given its essential role as a negative checkpoint for innate immunity and subsequent adaptive immunity, CD47-SIRPα axis has been explored as a new target for cancer immunotherapy and its disruption has demonstrated great therapeutic promise. Indeed, CD47 blocking antibodies have been found to decrease primary tumor size and/or metastasis in various pre-clinical models. In this review, we highlight the various functions of CD47, discuss anti-tumor responses generated by both the innate and adaptive immune systems as a consequence of administering anti-CD47 blocking antibody, and finally elaborate on the clinical potential of CD47 blockade. We argue that CD47 is a checkpoint molecule for both innate and adaptive immunity for tumor evasion and is thus a promising target for cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: CD47; Cancer immunotherapy; Chemotherapy; Clinical trial; Dendritic cell; Macrophage; SIRPα; “Don’t eat me” signal.
Figures
References
-
- Reinhold MI, Lindberg FP, Plas D, Reynolds S, Peters MG, Brown EJ. In vivo expression of alternatively spliced forms of integrin-associated protein (CD47) J Cell Sci. 1995;108(Pt 11):3419–3425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

