Extracellular microRNA signature in chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 28077372
- PMCID: PMC5495885
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00569.2016
Extracellular microRNA signature in chronic kidney disease
Abstract
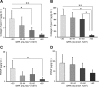
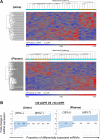
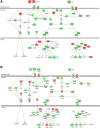
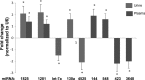
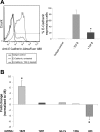
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are noncoding RNAs that regulate posttranscriptional gene expression. In this study we characterized the circulating and urinary miRNA pattern associated with reduced glomerular filtration rate, using Affymetrix GeneChip miR 4.0 in 28 patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Top miRNA discoveries from the human studies were validated in an Alb/TGFβ mouse model of CKD, and in rat renal proximal tubular cells (NRK52E) exposed to TGFβ1. Plasma and urinary levels of procollagen III N-terminal propeptide and collagen IV were elevated in patients with decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Expression of 384 urinary and 266 circulatory miRNAs were significantly different between CKD patients with eGFR ≥30 vs. <30 ml·min-1·1.73 m-2 Pathway analysis mapped multiple miRNAs to TGFβ signaling-related mRNA targets. Specifically, Let-7a was significantly downregulated, and miR-130a was significantly upregulated, in urine of patients with eGFR <30; miR-1825 and miR-1281 were upregulated in both urine and plasma of patients with decreased eGFR; and miR-423 was significantly downregulated in plasma of patients with decreased eGFR. miRNA expression in urine and plasma of Alb/TGFβ mice generally resembled and confirmed most, although not all, of the observations from the human studies. In response to TGFβ1 exposure, rat renal proximal tubular cells overexpressed miR-1825 and downregulated miR-423. Thus, miRNA are associated with kidney fibrosis, and specific urinary and plasma miRNA profile may have diagnostic and prognostic utility in CKD.
Keywords: TGFβ; chronic kidney disease; fibrosis.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Araki S, Haneda M, Koya D, Isshiki K, Kume S, Sugimoto T, Kawai H, Nishio Y, Kashiwagi A, Uzu T, Maegawa H. Association between urinary type IV collagen level and deterioration of renal function in type 2 diabetic patients without overt proteinuria. Diabetes Care 33: 1805–1810, 2010. doi: 10.2337/dc10-0199. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang CJ, Hsu CC, Chang CH, Tsai LL, Chang YC, Lu SW, Yu CH, Huang HS, Wang JJ, Tsai CH, Chou MY, Yu CC, Hu FW. Let-7d functions as novel regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistant property in oral cancer. Oncol Rep 26: 1003–1010, 2011. doi: 10.3892/or.2011.1360. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen PY, Qin L, Barnes C, Charisse K, Yi T, Zhang X, Ali R, Medina PP, Yu J, Slack FJ, Anderson DG, Kotelianski V, Wang F, Tellides G, Simons M. FGF regulates TGFβ signaling and endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition via control of let-7 miRNA expression. Cell Reports 2: 1684–1696, 2012. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.10.021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

