Ibrutinib Therapy Increases T Cell Repertoire Diversity in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
- PMID: 28077600
- PMCID: PMC5296363
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601190
Ibrutinib Therapy Increases T Cell Repertoire Diversity in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Abstract
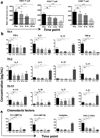
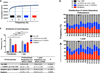
The Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib is a highly effective, new targeted therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) that thwarts leukemia cell survival, growth, and tissue homing. The effects of ibrutinib treatment on the T cell compartment, which is clonally expanded and thought to support the growth of malignant B cells in CLL, are not fully characterized. Using next-generation sequencing technology, we characterized the diversity of TCRβ-chains in peripheral blood T cells from 15 CLL patients before and after 1 y of ibrutinib therapy. We noted elevated CD4+ and CD8+ T cell numbers and a restricted TCRβ repertoire in all pretreatment samples. After 1 y of ibrutinib therapy, elevated peripheral blood T cell numbers and T cell-related cytokine levels had normalized, and T cell repertoire diversity increased significantly. Dominant TCRβ clones in pretreatment samples declined or became undetectable, and the number of productive unique clones increased significantly during ibrutinib therapy, with the emergence of large numbers of low-frequency TCRβ clones. Importantly, broader TCR repertoire diversity was associated with clinical efficacy and lower rates of infections during ibrutinib therapy. These data demonstrate that ibrutinib therapy increases diversification of the T cell compartment in CLL patients, which contributes to cellular immune reconstitution.
Copyright © 2017 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The remaining authors declared no competing financial interests.
Figures

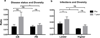

References
-
- Chiorazzi N, Rai KR, Ferrarini M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. The New England journal of medicine. 2005;352:804–815. - PubMed
-
- Burger JA, Buggy JJ. Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib (PCI-32765) Leukemia & lymphoma. 2013;54:2385–2391. - PubMed
-
- Messmer BT, Messmer D, Allen SL, Kolitz JE, Kudalkar P, Cesar D, Murphy EJ, Koduru P, Ferrarini M, Zupo S, Cutrona G, Damle RN, Wasil T, Rai KR, Hellerstein MK, Chiorazzi N. In vivo measurements document the dynamic cellular kinetics of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. The Journal of clinical investigation. 2005;115:755–764. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bagnara D, Kaufman MS, Calissano C, Marsilio S, Patten PE, Simone R, Chum P, Yan XJ, Allen SL, Kolitz JE, Baskar S, Rader C, Mellstedt H, Rabbani H, Lee A, Gregersen PK, Rai KR, Chiorazzi N. A novel adoptive transfer model of chronic lymphocytic leukemia suggests a key role for T lymphocytes in the disease. Blood. 2011;117:5463–5472. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pascutti MF, Jak M, Tromp JM, Derks IA, Remmerswaal EB, Thijssen R, van Attekum MH, van Bochove GG, Luijks DM, Pals ST, van Lier RA, Kater AP, van Oers MH, Eldering E. IL-21 and CD40L signals from autologous T cells can induce antigen-independent proliferation of CLL cells. Blood. 2013;122:3010–3019. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

